The Food Canning Industry Was Revolutionized In 1920, When The Continuous Rotary Pressure Sterilizer Was Introduced By Albert R. Thompson. Thompson Was Chief Engineer For The Anderson-Barngrover Co. Of San Jose, California, Now The FMC Corporation. The Sterilizer Cooked Canned Products Uniformly Under Pressure For Short Period At High Temperatures, Then Quickly Cooled Them Under Pressure To Prevent Swelling Or Bursting. It Operated Continuously At Speeds Of Up To 400 Cans Per Minute.
Agricultural & Biological
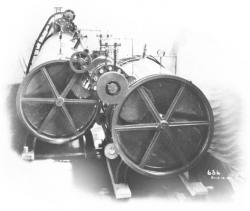
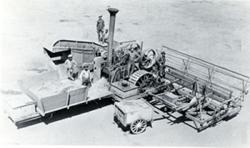
George Stockton Berry (1847-1917) of Lindsay, Tulare County, California designed, built, and in 1886, operated the first self-propelled combine. He was granted a U.S. Patent (# 374,339) in1887. The Berry design embodied the following "firsts":

The First Successful Row Crop Tractor Invented by Bert R. Benjamin (ASAE Member) was Operated and Tested on this Farm in 1923. Increased Row Crop Clearance and Overall Versatility Extending the Use of the Tractor to Cultivating, Accelerated the Conversion from Animal Power to Machine and Marked a New Era in American Agricultural Efficiency and Productivity. Dedicated by The American Society of Agricultural Engineers 1980

Designated an Historic Landmark in Honor of J. Brownlee Davidson a Founder of Agricultural Engineering First President of American Society of Agricultural Engineers Organizer of the First Professional Agricultural Engineering Curriculum July 1905 by American Society of Agricultural Engineers

Charles C. Fenno Of Grinnell, Ia, Patented The First Field Corn Silage Harvester On April 19, 1892. His Ground-Powered Machine Cut The Corn Plant And Fed The Tassel End First To A Rotary Cutter. Joseph Weigel Of Flandreau, Sd, Improved Fenno's Harvester In 1912 By Adding An Engine To Power The Cutter And By Feeding The Stalks Butt End First. Andrean And Adolph Ronning, Farmers Of Boyd, Mn Patented Further Improvements In 1915. In 1918 The American Harvester Co. Of Minneapolis, Mn, Began Manufacturing The Horse-Drawn Ronning Harvester Using Weigel's Patent Too.

This Creative Development Which Was Responsible For The Survival Of The Cotton Industry In The United States Occurred In General Nathaniel Greene's Plantation Near Savannah 10 Miles Northeast Of This Marker. Separation By Hand Labor Of The Lint From The Seed Of The Desired Upland Variety Of Cotton Produced Only One Pound Per Day Per Person. Eli Whitney, A Native Of Massachusetts And Yale Law Graduate, Came To Georgia To Teach School In Late 1792, At Age 27. Mrs. Catherine Greene, Widow Of General Greene, Invited Whitney To Her Plantation, And Urged Him To Design A Cotton Gin.
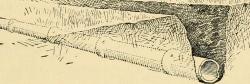
Farm And Residence of John Johnston 1791 - 1880 Eminent Farmer Who Here Originated Tile Underdrainage in America in 1835 and Thereby Became an Outstanding Contributor to Human Welfare Honored by The American Society of Agricultural Engineers 1935. Erected by State Education Department

Established in 1907, the American Society of Agricultural Engineers (ASAE) was managed by volunteers. In 1925, local editor Raymond Olney was named secretary, thus establishing ASAE in this area. By 1969, with over 7,000 members in 100 countries, an ASAE building was constructed at this site in St. Joseph, Mi. In 2005, ASAE became ASABE to recognize the importance of biology in the profession. ASABE collects and maintains the unique body of knowledge for the agricultural/biological engineering profession.

Designated an Historic Landmark of Agricultural Engineering. In the Shelbyville Area During the Spring of 1929, Raymore McDonald Designed and Developed the First Commercial Pick-Up Baler as Conceived and Financed by Horace Tallman and His Sons, Leslie R. and Gentry L. These Balers were Marketed for Many Years by the Ann Arbor Machine Company of Shelbyville. This Concept of Field Processing of Farm Forages Made a Significant Contribution to the Efficiency and Economy of Mechanized Forage Harvesting in the World's Agriculture.

In 1932, J. O. Smith, Agricultural Engineer at Delta Branch Experiment Station in Stoneville, MS, attached a small anhydrous ammonia cylinder to a plow in such a manner that the NH3 was released in the soil. The plow, a Georgia Stock, was pulled by a gray mule named Ike. This was the first known use of anhydrous ammonia as a soil-applied crop fertilizer. The crude apparatus and the anhydrous ammonia it applied provided a much needed source of nitrogen for the otherwise rich alluvial soils of the Mississippi Delta.


