The Williams-Miles History of Chemistry Collection, established in 1992, is one of the leading historical collections of chemistry books in the southern United States. It represents a combined 70 years of scholarly collecting by Wyndham D. Miles, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, and William D. Williams, Professor of Chemistry at Harding University. More than 2,000 volumes published between 1600 and 1900 are preserved here; the collection is particularly strong in 19th-century works.
National Institutes of Health


In 1961, in the National Institutes of Health Headquarters (Bethesda, MD), Marshall Nirenberg and Heinrich Matthaei discovered the key to breaking the genetic code when they conducted an experiment using a synthetic RNA chain of multiple units of uracil to instruct a chain of amino acids to add phenylalanine. The uracil (poly-U) served as a messenger directing protein synthesis. This experiment demonstrated that messenger RNA transcribes genetic information from DNA, regulating the assembly of amino acids into complex proteins.
Innovations
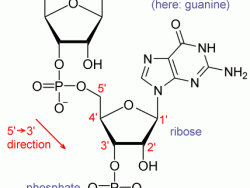
In 1961, in the National Institutes of Health Headquarters (Bethesda, MD), Marshall Nirenberg and Heinrich Matthaei discovered the key to breaking the genetic code when they conducted an experiment using a synthetic RNA chain of multiple units of uracil to instruct a chain of amino acids to add…
Read More
The Williams-Miles History of Chemistry Collection, established in 1992, is one of the leading historical collections of chemistry books in the southern United States. It represents a combined 70 years of scholarly collecting by Wyndham D. Miles, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland…
Read More

