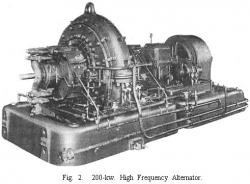
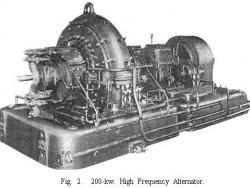
On 24 December 1906, the first radio broadcast for entertainment and music was transmitted from Brant Rock, Massachusetts to the general public. This pioneering broadcast was achieved after years of development work by Reginald Aubrey Fessenden (1866-1932) who built a complete system of wireless transmission and reception using amplitude modulation (AM) of continuous electromagnetic waves. This technology was a revolutionary departure from transmission of dots and dashes widespread at the time.
Radio


On the morning of 17 April 1967, radio astronomers used this radiotelescope at DRAO and a second one at the Algonquin Radio Observatory located 3074 km away to make the first successful radio astronomical observations using Very Long Baseline Interferometry. Today, VLBI networks span the globe, extend into space and continue to make significant contributions to both radio astronomy and geodesy.

The first use of wireless telegraphy in the field occurred during the Anglo-Boer War (1899-1902). The British Army experimented with Marconi's system and the British Navy successfully used it for communication among naval vessels in Delagoa Bay, prompting further development of Marconi's wireless telegraph system for practical uses. The Anglo-Boer War of 1899-1902 will be remembered as the last of the gentleman's wars, the war that marked the end of the Victorian era.



Innovations




The first use of wireless telegraphy in the field occurred during the Anglo-Boer War (1899-1902). The British Army experimented with Marconi's system and the British Navy successfully used it for communication among naval vessels in Delagoa Bay, prompting further development of Marconi's…
Read More
On the morning of 17 April 1967, radio astronomers used this radiotelescope at DRAO and a second one at the Algonquin Radio Observatory located 3074 km away to make the first successful radio astronomical observations using Very Long Baseline Interferometry. Today, VLBI networks span the globe,…
Read More
On 24 December 1906, the first radio broadcast for entertainment and music was transmitted from Brant Rock, Massachusetts to the general public. This pioneering broadcast was achieved after years of development work by Reginald Aubrey Fessenden (1866-1932) who built a complete system of wireless…
Read More

