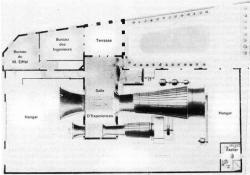
Late in life, the renowned structural engineer Gustave Eiffel (1832-1923) embarked on aeronautical research. Reliable data and repeatable research methods were rare in the early 1900s, but Eiffel brought an engineer's discipline to the field. In the process, he produced the most accurate aeronautical data of the time, confirmed a long-held theory about fluid flow that had never been unequivocally proven, and established a laboratory that became a model for future practice.
ASME


Edison's simple and unprecedented instrument allowed for the first time the permanent recording and reproduction of sound, especially the human voice. On December 6, 1877, Edison put tinfoil around the cylinder, turned the handle of the shaft and, shouting into one of the diaphragms, recorded a verse of Mary Had a Little Lamb "almost perfectly." From this machine evolved the phonographs and record industries of the world.

This dynamo, connected directly to a high-speed steam engine, was one of six that produced direct current at Thomas A. Edison's electric power station at 257 Pearl Street in New York City. The Pearl Street Station was the prototype for central station power generation. Edison set out in 1878 to provide an electrical distribution system to bring lighting into the home: His first filament lamp lit on October 21, 1879. With the help of Frances Upton and C.L. Clarke, Edison built his engine-driven dynamo for the 1881 Paris Electrical Exposition.
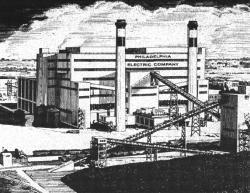
Operated by the Philadelphia Electric Company (PECO), now known as Exelon Corp., Eddystone Station Unit #1 is a 325 MW pulverized-coal-fired plant that pushed the technology of steam-electric generating plants. When built in 1960, engineers sought to make a more efficient plant using higher temperatures and pressures and larger machines. Previous experience at Philo 6 (Zanesville, Ohio, 1957) had demonstrated supercritical steam plants would work, so engineers pushed beyond that frontier to even larger machines and efficiencies.

Designed by Sam Diescher, son-in-law of the Monongahela's designer John Endres, the Duquesne Incline opened May 20, 1877, as the second of seventeen built and operated in the Pittsburgh area. It has operated with only minor interruptions for the last one hundred years. A preservation group from Duquesne Heights and Mount Washington interceded in 1962 to refurbish this incline to working order. Like the Monongahela, the Duquesne was steam powered and then converted to electric and updated with modern safety devices.



The concept of heating a number of buildings in the core area of a city from a single heating plant was introduced into the United States by Birdsill Holly at Lockport, New York, in 1877. The gain in thermal efficiency of a single large steam plant over a series of small isolated boilers led to widespread commercial installation of district heating. Organized by the Detroit Edison Company, the Central Heating Company began service here in 1903, supplying twelve customers with steam piped from the Edison Company's Willis Avenue Plant. Today's greatly enlarged system continues in operation.

BBethesdaState: MDZip: 20817Country: USAWebsite: http://www.asme.org/about-asme/history/landmarks/topics-m-z/research-and-development/-197-david-taylor-model-basin-%281939%29Creator: Taylor, David

HaarlemmermeerCountry: NetherlandsWebsite: http://www.asme.org/about-asme/history/landmarks/topics-m-z/pumping/-153-cruquius-pumping-station-%281849%29Creator: Cruquius, Nicolaus Samuel , Beijerinck, Jan Anne
This is one of three nearly identical pumping stations that drained the Haarlemmermeer (Haarlem Lake), 1849- 52, then continued to maintain the polder's water table for more than 80 years. The Haarlemmermeer area covers 45,000 acres (about 70 square miles) in a triangular region between the cities of Amsterdam, Haarlem, and Leiden.


