The U.S.S. Olympia is one of the two surviving ships of the era of the vertical reciprocating steam engine. The Cruiser Olympia, launched in 1892, was one of the first naval ships to be built with these engines. As part of the new American steel Navy, the construction of the Olympia was authorized in 1888 as cruiser number 6. As part of a Congressionally-mandated program to establish complete domestic capability for warship construction, the ship's contract was awarded to the Union Iron Works of San Francisco.
ASME


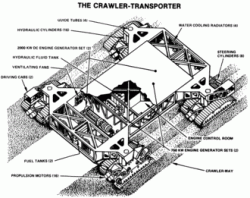
The crawler-transporters, formally known as the Missile Crawler Transporter Facilities, are a pair of tracked vehicles used to transport spacecraft from NASA's Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) along the Crawlerway to Launch Complex 39. They were originally used to transport the Saturn IB and Saturn V rockets during the Apollo, Skylab and Apollo-Soyuz programs. They were then used to transport Space Shuttles from 1981 to 2011. The crawler-transporters carry vehicles on the mobile platform launchers used by NASA, and after each launch return to the pad to take the platform back to the VAB.
The Broadmoor Manitou and Pikes Peak Cog Railway (also known as the Pikes Peak Cog Railway) is a cog railway that climbs one of the most iconic mountains in the United States, Pikes Peak in Colorado. The base station is in Manitou Springs, near Colorado Springs.
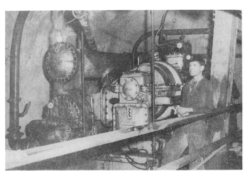
The Magma Copper Mine AC system designed by the Carrier Corporation was the first underground mechanical air conditioning system in North America. The initial installation of refrigerated cooling equipment in the Magma Mine at Superior, Arizona was necessary due to the increase in temperature lower into the mine. Below the 2000-foot level, the increase in rock temperature is approximately 1½ degrees F. per 100 feet of depth. The rock temperature on the 2000-foot level is 109°.
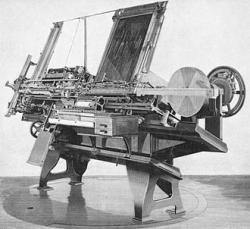
The Paige Compositor was an invention developed by James W. Paige (1842–1917) between 1872 and 1888. It was designed to replace the human typesetter of a lead type-composed printing form with a mechanical arm. In the early 1890s, a group of inventors signed a contract with Towner K.

The U.S.S. Texas is the last surviving warship of its kind--powered by reciprocating steam engines. It was built during a period in which naval authorities were switching to the newly-developed steam turbine for propulsion, but were unsure of its suitability. Only one more warship, the New York, commissioned one month after the Texas, was to be powered by the reciprocating engines.
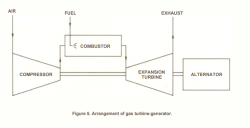
The Belle Isle gas turbine was installed in 1949 and was the first gas turbine built in the United States for the purpose of generating electric power. Its low cost and consistency aroused considerable interest in the electric utility industry, both here and abroad.

The Portsmouth Navy Yard is a United States Navy shipyard in Kittery on the southern boundary of Maine near the city of Portsmouth, New Hampshire. Founded in 1800, PNS is U.S. Navy's oldest continuously operating shipyard. Today, most of its work concerns the overhaul, repair, and modernization of submarines. he Portsmouth Naval Shipyard was established on June 12, 1800, during the administration of President John Adams.

The Edger station was the first steam electric plant produced that could tolerate over 1000 psi of pressure. Initially conceived by Mr. Irving Edwin Moultrop, then Assistant Superintendent, Construction Bureau of the Edison Electric Illuminating Company of Boston. He guided his company and the electric utility industry on a major step forward into the higher-pressure range of 1,200 psi steam.

First Land Vehicle to Exceed the Speed of Sound; averaged 763.04 mph
Innovations

The ABACUS II, designed and built by Texas Instruments, was the first practical automated production machine for the assembly of integrated circuits. Using heat and pressure, it bonded fine gold wire to microscopic contacts on the silicon chip and pin connections on the package.
The…
Read More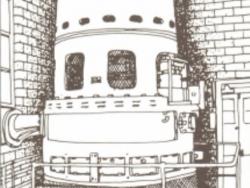
This, the first Curtis vertical turbine built, was constructed by the General Electric Co. for the Newport & Fall River Street Railway Co. It operated in the Newport, R.I., generating station until June 1927. It was transferred to the Harding Street Station of the Indianapolis Power &…
Read More
In 1899, during the earliest days of the automobile revolution, A. O. Smith developed a new, lightweight steel car frame. Within a few short years, he was selling these frames to a “who’s who” of car makers including Cadillac, Oldsmobile, and Ford. A. O. Smith’s son, Lloyd Raymond, carried on…
Read More
This was a pioneering venture in mainline railroad electrification and was a proving ground for railroad electrification technology. It established single-phase alternating current as a technical and economical alternative to direct current. This concept exerted considerable influence over…
Read More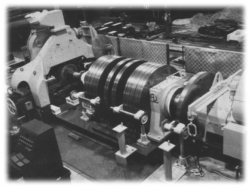
This inertia dynamometer is used to test railroad wheels under controlled conditions that can greatly exceed normal service. It is the first and only…
Read More
During the 1930's, research into advanced ballistic measurement techniques began at Aberdeen Proving Ground—the world's first large-scale, fully-instrumented ballistic range producing data on the aerodynamic characteristics of missiles in free flight.
Although this research had begun…
Read More
People thought inventor Walter Aiken was crazy when he proposed a railway to the top of Mt. Washington. Aiken built a model of the roadbed and track with a cog rail system, but entrepreneur Sylvester Marsh is credited for launching the Cog Railway and bringing Aiken's ideas to fruition.
… Read MoreThis machine, which began operation on December 15, 1891, for the New York Edison Illuminating Company, represents the beginning of large-scale electric power generation in the United States. The generator was designed by chief engineer John Van Vleck, David Joy (known in England for his valve…
Read More
This run-of-the-river plant is a typical example of late nineteenth-century small-scale (750 kilowatt) low-head hydroelectric power technology. The Fries Manufacturing and Power Company began operating the Idol's Station on April 18, 1898, making it the first commercial hydroelectric plant in…
Read More
This low-head operating plant is representative of nineteenth-century hydropower-plant practice using many small turbines in contrast to twentieth-century use of few large turbines and generators. Its 40,000 horsepower capacity made it the largest in the country using turbines of American design…
Read More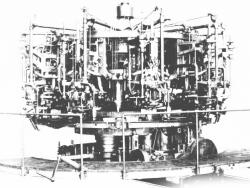
Only since 1912 have glass jars and bottles been in cheap and plentiful supply for pharmaceuticals, household products, food and beverages, and an endless variety of uses. The bottle-making machine introduced the safety, standardization, quality, and convenience of glass containers. Not only did…
Read More
The largest mine hoist in the world, it serves the two incline skipways of Shaft No. 2, almost 9,300 feet long. The overhead winding drum has a diameter of 30 feet, of which the cylindrical center section is 10 feet long. The two 10-foot long end sections taper down to a 15-foot diameter. Wire…
Read More
The Connecticut Light & Power Company pioneered the use of pumped storage in the United States at this hydroelectric station. First operated in 1929, the Rocky River Plant had two reversible pumps that somewhat resemble large hydroelectric turbines. This permitted significant improvements in…
Read More
America's first practical helicopter, it pioneered the single main rotor concept that became the predominant helicopter configuration throughout the world. The principles that were developed and demonstrated by the VS-300 had direct application in the design of the early mass-production…
Read MoreThe Wildcat's innovative "Sto-Wing" mechanism developed on the XF4F-4 prototype by Leroy (Roy) Grumman (1895-1982), a founder of Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation, was crucial to the U. S. Navy's success during World War II.
The idea of a folding wing was not new: as early as 1920…
Read More
Developed for use in both the plains and mountains, this coal-fired passenger locomotive was among the most advanced in design, construction, and performance of any 4-8-4. Designed by Norfolk & Western engineers and built in the Norfolk & Western Roanoke shops, the 611 was specially…
Read More
The 4,620-horsepower GG1 was primarily a passenger locomotive, routinely operating at over 100 miles per hour, but was used in freight service as well. Conceived by the Pennsylvania Railroad and built by the Baldwin Locomotive Works and General Electric Company, No. 4800 logged nearly 5 million…
Read More
The articulated wheel-base steam locomotive represents the final phase of steam locomotive development in size and power. The cab-in-front feature was widely used by the Southern Pacific Railroad beginning in 1909 to alleviate smoke and heat problems for locomotive personnel en route through…
Read More
The refrigeration units placed on trucks in 1938 by Thermo King Corp. revolutionized the transportation of perishable foods. Today they are a common sight on streets everywhere. Consumer demand for meat, poultry, produce and dairy products increased at an astounding rate. These installations and…
Read More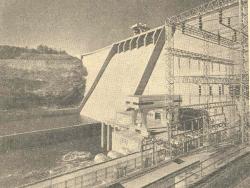
The integration of pump and turbine was the first of many to be installed in power-plant systems in the United States. It was the largest and most powerful in the world. As a "pump storage" unit in the Tennessee Valley Authority's system, it effected significant economies in the generation of…
Read More

