Referred to as the "catalyst of the Industrial Revolution," textile manufacturing helped to transform the American economy from an agricultural to a manufacturing economy. It led to transitions from human to mechanical power and from wood to metal construction. Population shifts resulted from significant numbers of people moving from rural areas to work in urban factories. The collection of tools and machinery housed at the American Textile History Museum (ATHM) represents a collection of ideas which developed during this period.
1960
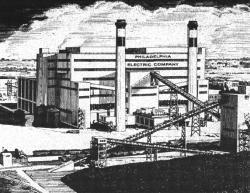
Operated by the Philadelphia Electric Company (PECO), now known as Exelon Corp., Eddystone Station Unit #1 is a 325 MW pulverized-coal-fired plant that pushed the technology of steam-electric generating plants. When built in 1960, engineers sought to make a more efficient plant using higher temperatures and pressures and larger machines. Previous experience at Philo 6 (Zanesville, Ohio, 1957) had demonstrated supercritical steam plants would work, so engineers pushed beyond that frontier to even larger machines and efficiencies.
Innovations

Operated by the Philadelphia Electric Company (PECO), now known as Exelon Corp., Eddystone Station Unit #1 is a 325 MW pulverized-coal-fired plant that pushed the technology of steam-electric generating plants. When built in 1960, engineers sought to make a more efficient plant using higher…
Read MoreReferred to as the "catalyst of the Industrial Revolution," textile manufacturing helped to transform the American economy from an agricultural to a manufacturing economy. It led to transitions from human to mechanical power and from wood to metal construction. Population shifts resulted from…
Read More

