This was a pioneering venture in mainline railroad electrification. It established single-phase alternating current as a technical and economical alternative to direct current. This concept exerted considerable influence over subsequent systems both in the United States and abroad. The major components of the system were developed by the engineering staffs of the New York, New Haven & Hartford Railroad and the Westinghouse Electric and Manufacturing Company of East Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.
USA


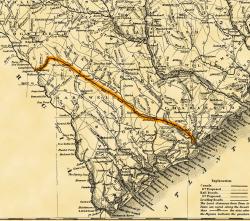
Built with a single set of tracks consisting of hardwood rails and wooden ties, and using wooden trestles to carry it over low-lying areas, the 136-mile Charleston-Hamburg Railroad was one of the longest railroads in the world when it was completed in 1833. It also became the first railroad in the United States to be powered entirely by steam, the first to carry mail under contract, and the first to provide regularly scheduled passenger service.

In an era when roads and canals were the most common means of overland transportation, the Allegheny Portage Railroad provided a novel alternative. The railway carried fully-loaded canal boats over the steep grades of the Allegheny Mountain. The 36-mile system rose almost 2,300 feet above sea level at its summit - the highest level to which canal boats had ever been carried. The project included ten double-tracked inclined planes, powered by steam engines. Its 900-foot Staple Bend Tunnel, cut from solid rock, was the first railroad tunnel constructed in America.


The Alaska Highway, initially called the Alaskan-Canadian (Alcan) Military Highway, provided an essential transportation link to the Yukon and Alaska during World War II. It begins at the junction with several Canadian highways in Dawson Creek, British Columbia and runs to Delta Junction, Alaska, via Whitehorse, Yukon. After the shock of Pearl Harbor, the Alaska Highway was a first step in America's defense strategy -- a vital military supply line during the war. Over ten thousand Army Engineers were rushed to the far Northwest.

This 50,000-ton die-forging press is among the largest fabrication tools in the world. It was designed and built for the U.S. Air Force by the Mesta Machine Company of Pittsburgh, following the discovery of a 30,000-ton press used by the Germans in World War II (later acquired by the Soviet Union). By 1950, a Heavy Press Program was organized to establish a self-sustaining industrial base for a press capable of producing large forgings and extrusions for the United States. The 50,000-ton Mesta press was one of the first built under this program between 1952 and 1955.

This is one of the earliest uses of engineered water supply and irrigation systems in the United States. The first of eight original acequias was under construction in 1718 and two are still in operation. The remains of one are visible on the grounds of the Alamo. The Acequias of San Antonio are among the earliest engineered water supply and irrigation systems recorded in the United States. The Acequias served an integral role in the growth and stability of the San Antonio community for nearly 200 years.

A majority of the buildings, used originally in steam locomotive repair and maintenance, are still intact, including the backshop (erecting shop), roundhouse, flue shop, paint shop, and parts storage buildings. The 37-stall roundhouse is one of the largest remaining roundhouses in North America still in continuous operation. The site contains other significant buildings including the car repair shed, yard office, oil house, sand house, and wheel balancing shed.

Designed in 1873 by Christopher Latham Sholes, with Carlos Glidden, Samuel Soulé and Mathias Schwalbach, the Sholes & Glidden 'Type Writer' was the first commercially successful device that rapidly printed alphanumeric characters on paper in any order.


