Morris Canal was built to transport coal from the Lehigh Valley of Pennsylvania to industrial markets in Newark and New York. The total length of the canal was 106 miles. The canal climbed an astonishing 914 feet from Newark Bay to the summit at Lake Hopatcong, and then dropped 760 feet to the Delaware River at Phillipsburg. This gave the canal an average vertical slope of 18 feet per mile, steep compared to the contemporary Erie Canal's relatively gentle slope of one foot per mile.
New York


In the 19th century, New York City was a burgeoning industrial and commercial metropolis - the largest city in the United States and second largest in the world. As the city's population increased, people began to call for construction of an underground railway. Many unusual engineering challenges had to be overcome, not the least of which was construction in a dense urban area. After lengthy legal battles over property rights and the debt limit of the city, ground was broken on March 24, 1900.

Nicholas Montgomery Powers built the bridge. It was first constructed behind the village, then taken apart and reassembled over the stream. Some residents questioned the idea of re-constructing it, but Powers was so confident of the bridge's durability that he sat on the roof when the final trestles supporting it were removed. From his perch he reportedly said: "If the bridge goes down, I never want to see the sun rise again!"

The longest steel-arch bridge in the world for 46 years, the Bayonne Bridge continues to be celebrated today as a major aesthetic and technical achievement. The 1,675-foot bridge replaced a ferry service which until then was the only means of crossing from the Bayonne peninsula to Staten Island. While providing this essential link in the transportation network of greater New York City, the bridge's mid-span clearance of 150 feet also allows for unobstructed navigation on Newark Bay, the main shipping channel to the inland ports of Newark and Elizabeth, New Jersey.

This was a pioneering venture in mainline railroad electrification. It established single-phase alternating current as a technical and economical alternative to direct current. This concept exerted considerable influence over subsequent systems both in the United States and abroad. The major components of the system were developed by the engineering staffs of the New York, New Haven & Hartford Railroad and the Westinghouse Electric and Manufacturing Company of East Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.
This machine, which began operation on December 15, 1891, for the New York Edison Illuminating Company, represents the beginning of large-scale electric power generation in the United States. The generator was designed by chief engineer John Van Vleck, David Joy (known in England for his valve gear), and S. F. Prest.
Innovations
This machine, which began operation on December 15, 1891, for the New York Edison Illuminating Company, represents the beginning of large-scale electric power generation in the United States. The generator was designed by chief engineer John Van Vleck, David Joy (known in England for his valve…
Read More
This was a pioneering venture in mainline railroad electrification. It established single-phase alternating current as a technical and economical alternative to direct current. This concept exerted considerable influence over subsequent systems both in the United States and abroad. The major…
Read More
The longest steel-arch bridge in the world for 46 years, the Bayonne Bridge continues to be celebrated today as a major aesthetic and technical achievement. The 1,675-foot bridge replaced a ferry service which until then was the only means of crossing from the Bayonne peninsula to Staten Island…
Read More
Nicholas Montgomery Powers built the bridge. It was first constructed behind the village, then taken apart and reassembled over the stream. Some residents questioned the idea of re-constructing it, but Powers was so confident of the bridge's durability that he sat on the roof when the final…
Read More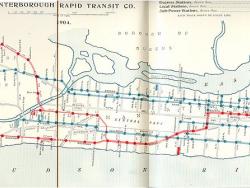
In the 19th century, New York City was a burgeoning industrial and commercial metropolis - the largest city in the United States and second largest in the world. As the city's population increased, people began to call for construction of an underground railway. Many unusual engineering…
Read More
Morris Canal was built to transport coal from the Lehigh Valley of Pennsylvania to industrial markets in Newark and New York. The total length of the canal was 106 miles. The canal climbed an astonishing 914 feet from Newark Bay to the summit at Lake Hopatcong, and then dropped 760 feet to the…
Read More

