Published in 1914-15, the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC) was the first comprehensive standard for the design, construction, inspection, and testing of boilers and pressure vessels. With adoption in the United States and use in many countries, it has contributed significantly to public safety and influenced the continued development of boiler and pressure vessel technology.
USA


The Southwest Research Institute Split-Hopkinson Pressure Bar apparatus is a mechanical test instrument used to characterize the dynamic response of materials at high strain rates (typical of impacts and explosions).
The apparatus, based on devices invented by Bertram Hopkinson and Herbert Kolsky, was developed at SwRI in 1962 by Dr. Ulric Lindholm. Initially created to evaluate the behavior of metals under various conditions, the SwRI Split-Hopkinson Pressure Bar has since been applied to a wide range of materials.

This hydraulic closed-die press, among the largest fabrication tools in the world, has had a profound influence in America's leading role in commercial aircraft, military aircraft, and space technology. As part of the same Heavy Press Program that created the Mesta press, the Wyman-Gordon press was designed by the Loewy Construction Company and began operating in October 1955. Among its contributions was the development of the new jetliner Boeing 747 in the 1960s.

The world's first high-speed, dockside container-handling cranes reduced ship turnaround time from three weeks to eighteen hours. They became the model and set the standard for future designs worldwide. In service January 7, 1959, the A-frame cranes built at Encinal Terminals in Alameda, California, were designed to move large quantities of products with less handling, less damage, and less pilferage. Under the leadership of C. Dean Ramsden, P.E., the Pacific Coast Engineering Company (PACECO Inc.) met performance specifications developed by the Matson Navigation Company.

The IBM 350 disk drive storage development led to the breakthrough of on-line computer systems by providing the first storage device with random access to large volumes of data. Since its introduction on September 4, 1956, it has become the primary computer bulk-storage medium, displacing punched cards and magnetic tapes and making possible the use of the computer in such areas as airline reservations, automated banking, medical diagnosis, and space flights.
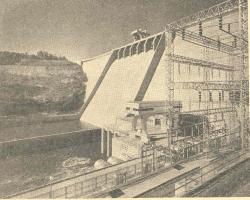
The integration of pump and turbine was the first of many to be installed in power-plant systems in the United States. It was the largest and most powerful in the world. As a "pump storage" unit in the Tennessee Valley Authority's system, it effected significant economies in the generation of electrical energy. The unit was designed by engineers of the Tennessee Valley Authority and the Allis-Chalmers Company. It was built by Allis-Chalmers.
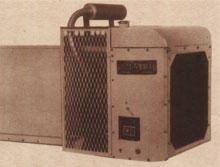
The refrigeration units placed on trucks in 1938 by Thermo King Corp. revolutionized the transportation of perishable foods. Today they are a common sight on streets everywhere. Consumer demand for meat, poultry, produce and dairy products increased at an astounding rate. These installations and subsequent ones on refrigerated vehicles, ships, and railroads have had worldwide impact on the preservation of food and other perishables during distribution.

The articulated wheel-base steam locomotive represents the final phase of steam locomotive development in size and power. The cab-in-front feature was widely used by the Southern Pacific Railroad beginning in 1909 to alleviate smoke and heat problems for locomotive personnel en route through tunnels and snow sheds. This locomotive, built by the Baldwin Locomotive Works, operated between 1944 and 1956 before being displaced by a diesel-electric locomotive.

The 4,620-horsepower GG1 was primarily a passenger locomotive, routinely operating at over 100 miles per hour, but was used in freight service as well. Conceived by the Pennsylvania Railroad and built by the Baldwin Locomotive Works and General Electric Company, No. 4800 logged nearly 5 million miles in its forty-five-year life. It was the prototype for a 139-unit fleet built during a decade to serve on the PRR's electrified lines, and the only one with a riveted body shell; the remainder were welded.

Developed for use in both the plains and mountains, this coal-fired passenger locomotive was among the most advanced in design, construction, and performance of any 4-8-4. Designed by Norfolk & Western engineers and built in the Norfolk & Western Roanoke shops, the 611 was specially balanced to minimize rail damage at high speeds. No. 611, eleventh of fourteen constructed and the last survivor, was retired from service and donated to the Roanoke Transportation Museum in 1959.


