The plant began operation only twenty-six days after Thomas Edison's first steam plant began operating on Pearl Street in New York (NL 46). On September 30, 1882, an Edison "K" type dynamo produced electricity from a water-powered turbine to light three buildings (two paper mills and the H.J. Rogers home), at rate of about 12 1/2 kilowatts. It is the first Edison hydroelectric central station to serve a system of private and commercial customers in North America. The story of its development provides keen insight into the nation's first experiences with the electric light.
Hydroelectric


Located at the northern tip of Michigan where Lake Superior, Lake Michigan, and Lake Huron join together, the Sault Ste. Marie Hydroelectric Power Complex was built to harness the hydroelectric potential of the 20-foot falls at the headwaters of the St. Marys (sic) River, the sole outlet of Lake Superior. A century after its construction, the plant remains the largest low-head hydroelectric facility in the United States. Today, the Sault Ste. Marie plant supplies electricity to area residents, especially those in the Upper Peninsula of Michigan.


In 1918, the U.S. Reclamation Service's director and chief engineer Arthur P. Davis proposed a dam of unprecedented height to control the devastating floods on the Colorado River, generate hydroelectric power, and store the river's ample waters for irrigation and other uses.

The massive Grand Coulee Dam, on the Columbia River, is the largest concrete structure in the U.S., the largest hydroelectric facility in the U.S., and the sixth-largest hydroelectric facility in the world. It provides irrigation for up to 1.1 million acres of agricultural lands and the hydroelectric complex maintains a generating capacity of 6.8 million kilowatts. It also serves as the primary flood control for the Columbia River basin (with a capacity of 5.18 million acre-feet of water) and provides recreational opportunities on the 150-mile-long Franklin D. Roosevelt Lake.

The Georgetown Steam Plant, a surprisingly complete and operable steam power plant after a career of nearly seventy-five years, was built in the early 1900s when Seattle's inexpensive hydroelectric power attracted manufacturers. Much of the power produced at this plant operated the streetcars. It marks the beginning of the end of the reciprocating steam engine's domination in the growing field of electrical energy generation for lighting and power.

The largest rolled-earth fill dam in the world at the time of its completion, Denison Dam eventually served as a prototype for dam construction in future U.S. Army Corps of Engineers projects throughout the arid plains of the American Southwest. Procedures and equipment developed during its construction are now commonplace in the sampling and testing of soils.


Requests for public power in Seattle began in the late 1890s and lead to the voter approval for building the Cedar Falls Water Supply hydroelectric dam plant in 1902. The first municipally developed and owned hydroelectric plant in the United States began operation in October 1904. The facility is situated one-half mile below Cedar Lake (later known as Chester Morse Lake) near North Bend in King County.

The Connecticut Light & Power Company pioneered the use of pumped storage in the United States at this hydroelectric station. First operated in 1929, the Rocky River Plant had two reversible pumps that somewhat resemble large hydroelectric turbines. This permitted significant improvements in the system efficiency of the company's network of hydroelectric and thermal-electric power generating plants. Water is pumped uphill through a penstock and stored in Lake Candlewood.
Innovations

The Connecticut Light & Power Company pioneered the use of pumped storage in the United States at this hydroelectric station. First operated in 1929, the Rocky River Plant had two reversible pumps that somewhat resemble large hydroelectric turbines. This permitted significant improvements in…
Read More
Requests for public power in Seattle began in the late 1890s and lead to the voter approval for building the Cedar Falls Water Supply hydroelectric dam plant in 1902. The first municipally developed and owned hydroelectric plant in the United States began operation in October 1904. The facility…
Read More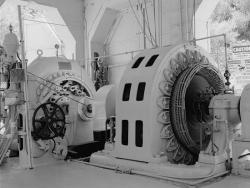

The largest rolled-earth fill dam in the world at the time of its completion, Denison Dam eventually served as a prototype for dam construction in future U.S. Army Corps of Engineers projects throughout the arid plains of the American Southwest. Procedures and equipment developed during…

The Georgetown Steam Plant, a surprisingly complete and operable steam power plant after a career of nearly seventy-five years, was built in the early 1900s when Seattle's inexpensive hydroelectric power attracted manufacturers. Much of the power produced at this plant operated the streetcars.…
Read More
The massive Grand Coulee Dam, on the Columbia River, is the largest concrete structure in the U.S., the largest hydroelectric facility in the U.S., and the sixth-largest hydroelectric facility in the world. It provides irrigation for up to 1.1 million acres of agricultural lands and the…
Read More
In 1918, the U.S. Reclamation Service's director and chief engineer Arthur P. Davis proposed a dam of unprecedented height to control the devastating floods on the Colorado River, generate hydroelectric power, and store the river's ample waters for irrigation and other uses. A dam project of…
Read More

Located at the northern tip of Michigan where Lake Superior, Lake Michigan, and Lake Huron join together, the Sault Ste. Marie Hydroelectric Power Complex was built to harness the hydroelectric potential of the 20-foot falls at the headwaters of the St. Marys (sic) River, the sole outlet of…
Read More
The plant began operation only twenty-six days after Thomas Edison's first steam plant began operating on Pearl Street in New York (NL 46). On September 30, 1882, an Edison "K" type dynamo produced electricity from a water-powered turbine to light three buildings (two paper mills and the H.J.…
Read More

