Conceived as one of the major structures on the Prussian Eastern Railway, the Old Wisla Bridge at Tczew originally consisted of six wrought iron spans. Due to Germany's invasion of Poland at the beginning World War II in 1939, only three original spans remain today. These remaining spans represent a unique technical monument of civil engineering achievements in the mid-nineteenth century.
1850-1859


The Whipple Bowstring Truss Bridge was built from a design patented in 1841 by Squire Whipple. Whipple was the first person to understand the stresses in truss members and he developed the first theoretical formula to calculate stresses in the articulated truss. His bowstring truss was the first to use cast iron for compression and wrought iron for tension membranes.

The history of this foundry, which was the oldest malleable iron company in continuous operation in the United States for many years, was inseparable from that of the small town of Westmoreland, where neighbors and workers kept time by the foundry bell. The firm was founded as Oakhill Malleable Iron Company in 1833 and was established under its present name in Westmoreland in 1850. Erastus W. Clark, who along with his brother-in-law Abel Buell brought the foundry to Westmoreland, ran the ironworks until 1871 and was the first of six generations who still own and manage it.

The Watertown Arsenal was the first major engineering testing laboratory in America. It was created to store and manufacture cutting-edge military technology and weaponry. The United States Army Research and Materials Laboratory continued to use the site until 1989, employing soldiers and civilians to produce and test artillery.

Beginning with the blacksmith shop of German immigrant Meinrad Rumely (1823-1904), this successive family of firms invented and produced a line of agricultural equipment that played a vital role in the evolution of farming based on the muscle of humans and animals to one based on the power of the steam and ultimately the internal-combustion engine. The M. & J. Rumely Co. became the M. Rumely Co., and then the Advance Rumely Co. The Allis-Chalmers Company acquired the business in 1931.

This reaction or "Scotch" turbine had as its antecedent the steam reaction wheel invented in Greek Alexandra by Hero around 100 B.C.. It found widespread hydraulic application in the United States from the beginning of the nineteenth century to mid-century when French-inspired hydraulic turbine design pushed reaction wheels into obsolence.



The drilling of this oil well marks the modern phase of the petroleum industry. A series of revolutionary technological changes, unforeseen even by the most prophetic, followed. Drake demonstrated practical oil recovery by applying salt-well drilling techniques, including the use of the derrick, and invented the modern method of driving iron pipe.

One of four single-track tunnels built by the Blue Ridge Railroad, the 4,273-foot Crozet Tunnel was constructed at a time when hand drills, pickaxes, and black powder amounted to state-of-the-art tunneling technology. At the time of its completion, it was the longest railroad tunnel in the world. Envisioned and built by Claudius Crozet, a French-born educator and civil engineer, the tunnel remains a testament to his belief in advancing rail transportation even when faced with numerous difficulties.
Innovations
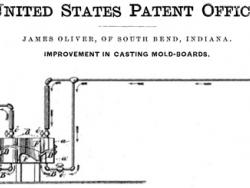
On June 30, 1857, James Oliver filed a patent application for chilling the wear face of cast-iron moldboard plows. While pouring molten cast iron in sand molds he circulated hot water through chillers to regulate the rate of cooling. Oliver's control of raw material content and…
Read More
The Old Lock Pump House, whose first element was built in 1837, preserves a feature of the old canal, which relied on locks and pumps to move vessels over the low divide of the Delmarva Peninsula between Chesapeake Bay and Delaware Bay. Because there are no large rivers on the peninsula, water…
Read More

