The idea of a canal eliminating the costly and dangerous sea trip around the Massachusetts peninsula of Cape Cod was envisioned as early as 1623 by Pilgrim leader Miles Standish. It was not until financier August Belmont became involved in 1906, however, that sufficient funds for the project could be raised. Belmont had been the primary backer of New York City's first subway, and chose the subway's chief engineer, William Barclay Parsons, as the canal's project director.
1900-1909


The Buffalo Bill Dam, known as the Shoshone Dam until 1946, was the first mass concrete dam in America. At nearly 325 feet high, it was also the tallest dam in the world at the time of completion.
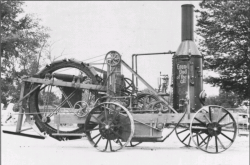
During the post-Civil War era, efforts to cultivate the land for higher crop yields resulted in the digging of thousands of miles of ditches to improve land drainage. Accurately graded ditches were needed for open drainage, pipeline trenches and placement of underground agricultural drainage tile. Teams of skilled workers laid out the direction and gradient of a ditch and dug it out with pick and shovel. The Black Swamp area, where Lake Erie drains into northwest Ohio and southeast Michigan, was the center of much of the U.S. ditching activity.

Bremen Airport was founded in 1909. In 1924, German aviation pioneers Henrich Focke and Georg Wulf founded the Focke-Wulf company on the site. On June 26, 1936, Heinrich Focke’s Fw 61, the world’s first fully operational helicopter, made a successful maiden flight at the airport, piloted by Ewald Rohlfs. Other aircraft developed at the site included the Fw 190 fighter plane, and Fa223 helicopter, both used by the German Luftwaffe in World War Two, as well the VAK 191B, an experimental fighter plane with vertical take-off and landing capabilities, developed in the 1970s.

This was a pioneering venture in mainline railroad electrification. It established single-phase alternating current as a technical and economical alternative to direct current. This concept exerted considerable influence over subsequent systems both in the United States and abroad. The major components of the system were developed by the engineering staffs of the New York, New Haven & Hartford Railroad and the Westinghouse Electric and Manufacturing Company of East Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.


The Glengyle is the earliest known survivor of the fleet of heavyweight, all-steel sleepers built by Pullman Company. The design was introduced in 1907 as a marked improvement over the wooden version then in use. Some 10,000 were built, in various configurations, the last in 1931. The Glengyle is original in its interior and most of its components.

This collection of equipment—all of it maintained in operating condition and used for educational purposes—was established in 1987. It spans the period from the late 19th century to the 1940s, when steam was the prime motive force for most U.S. industries, including rail and marine transportation. The collection of about 25 items (mostly stationary steam) includes a locomotive, switcher, and steam tractor: Locomotive #385 Consolidation 2-8-0 designed for fast freight service was built by Baldwin Locomotive Works of Philadelphia in November 1907 for the Southern Railway.
Works of Philadelphia, PA in 1907 for the
Southern Railway. Now part of the Bergen County Steam CollectionEra_date_from: 1900s

Published in 1914-15, the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC) was the first comprehensive standard for the design, construction, inspection, and testing of boilers and pressure vessels. With adoption in the United States and use in many countries, it has contributed significantly to public safety and influenced the continued development of boiler and pressure vessel technology.

The North Island Main Trunk Railway permitted overland travel and development of the New Zealand hinterland. Built under challenging conditions and over difficult terrain, all cuts, fills, and tunneling were minimized by careful use of the topography and by innovative engineering.
Over 30 miles south of Taumarunui, the North Island Main Trunk Railway climbs 2,086 feet to the edge of the great Waimarino Plateau. But over the last seven miles, an abrupt increase in altitude of over 700 feet posed an engineering challenge that led to the design of the famed Raurimu Spiral.


