The story is so improbable it defies belief: a soil sample from Japan stops suffering in Africa. It starts when a scientist discovers a lowly bacterium near a golf course outside Tokyo. A team of scientists in the United States finds that the bacterium produces compounds that impede the activity of nematode worms. It is developed into a drug that wards off parasites in countless pets and farm animals, averting billions of dollars in losses worldwide.
ACS


Long before Texas gushers and offshore drilling, and a century before oil wells dotted Arabian sands and rose out of Venezuelan waters, the center of petroleum production was western Pennsylvania. In the middle of the 19thcentury two developments occurred that guaranteed Pennsylvania’s dominance: The construction, in Pittsburgh, of the first still to refine crude oil into kerosene for use in lighting, and the drilling of the first oil well in Titusville, Pennsylvania.

DayGlo fluorescent pigments, a new class of pigments based on fluorescent dyes and polymeric materials, were developed between the 1930s and 1950s by scientists at Switzer Brothers, Inc. (now Day-Glo Color Corp.). These pigments absorb various light frequencies (visible and invisible to the human eye) and reemit them, producing intense visible colors that appear to glow, even in daylight.

By the 1950s, synthetic fabrics - often wrinkle resistant and flame retardant - began to overtake cotton as the dominant U.S. textile fiber. To reverse this trend chemists and chemical engineers at the Southern Regional Research Center initiated research to modify cotton chemically. Their efforts in developing agents that crosslinked the cellulose fibers and in establishing crosslinking mechanisms led to improved durable press fabrics. SRRC studies also developed new agents that improved the durability of flame retardant cotton to laundering.

Imagine a world without batteries. It would be a much different world, in which the automobile and the telephone would have developed differently and probably later, a world without many of the conveniences of modern life and without some of the necessities. The battery, ever smaller and more powerful, defines much of our modern comforts and advances. There were many scientific and technological advances on the way to those smaller and more powerful batteries.

Recent archaeological evidence reveals early Virginia, which included both the Roanoke and Jamestown colonies, as the birthplace of the American chemical enterprise. Chemical processes first applied experimentally at Roanoke were re-introduced at Jamestown twenty years later.

The Chemical Abstracts Service, a division of the American Chemical Society, has provided the most comprehensive repository of research in chemistry and related sciences for over 100 years. CAS innovations have fueled chemical research through development of the CAS RegistrySM and CAS databases which contain invaluable information for chemical scientists, including SciFinder® and STN®.

When Georgia chemist Charles Holmes Herty found a way to make quality paper from pine trees in 1932, he also founded an industry that brought much-needed jobs to the depression-crippled south. Paper producers had deemed the plentiful pine too gummy—until Herty's Savannah Pulp and Paper Laboratory wrote a new chapter in the ancient craft inspired by insects who built paper nests while dinosaurs roamed the earth. At its root, however, the papermaking process remained the same: the bonding of cellulose, a polymer whose long chains support plant cell walls.

In 1897, Dr. Alice Hamilton (1869-1970) came to Hull-House, a social settlement founded to address the needs of immigrants living on Chicago’s Near West Side. Through living and working in the Hull-House neighborhood, she identified occupational diseases plaguing those who worked in the “dangerous trades”: rubber, dyes, lead, enamelware, copper and mercury production, and explosives and munitions. Collaborating with the U.S. Department of Labor, Hamilton documented the occupational diseases from which these workers suffered.

Albert Szent-Györgyi (1893-1986), biochemist, pioneered the study of biological oxidation mechanisms during the 1920s. Between 1930 and 1936, while a Professor at Szeged University, he proved that hexuronic acid, which he had previously isolated, is identical with vitamin C and that it could be extracted in kilogram quantities from paprika.
Innovations

The Polymer Research Institute was established in 1946 by Herman F. Mark, a pioneer in the study of giant molecules. The Institute brought together a number of polymer researchers to create the first academic facility in the United States devoted to the study and teaching of polymer science.…
Read More
When Joseph Priestley discovered oxygen in 1774, he answered age-old questions of why and how things burn. An Englishman by birth, Priestley was deeply involved in politics and religion, as well as science. When his vocal support for the American and French revolutions made remaining in his…
Read More
In 1962 Neil Bartlett demonstrated the first reaction of a noble gas. The noble gas family of elements - helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon - had previously been regarded as inert. By combining xenon with a platinum fluoride, Bartlett created the first noble gas compound. This…
Read More

For more than a century, scientists at Rockefeller University have enhanced our understanding of the molecular basis of life — specifically the relationship between the structure and function of nucleic acids and proteins. They showed that DNA transfers genetic information and that the sugars…
Read More
In 1900, Moses Gomberg, Professor of Chemistry at the University of Michigan, confirmed the existence of a stable, trivalent organic free radical: triphenylmethyl. In so doing, he challenged the then prevailing belief that carbon could have only four chemical bonds. Gomberg’s discovery made a…
Read More
In the years 1926 to 1956, the German chemist Hermann Staudinger carried out his pathbreaking research on macromolecular chemistry in Freiburg. His theories on the polymer structures of fibers and plastics and his later research on biological macromolecules formed the basis for countless modern…
Read More
This research and development complex was established by the founders of Universal Oil Products (later named UOP) to develop key products for the oil-refining industry. The processes created here profoundly affected the refining, treatment and conversion of crude oil and the development of the…
Read More
The Williams-Miles History of Chemistry Collection, established in 1992, is one of the leading historical collections of chemistry books in the southern United States. It represents a combined 70 years of scholarly collecting by Wyndham D. Miles, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland…
Read More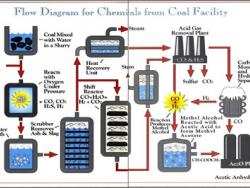
Chemicals from the Coal Facility of Eastman Chemical Company was the first in the United States to use coal rather than petroleum as a raw material in the commercial production of acetyl chemicals — important building blocks in the synthesis of a wide range of consumer products. The plant,…
Read More
Developed by Rohm and Haas in the 1940s, water-based acrylic emulsion technology filled a need for easy-to-use household paints for a growing suburban population in the United States following World War II. This aqueous technology required less preparation to use, was easier to clean up, had…
Read More
Albert Szent-Györgyi (1893-1986), biochemist, pioneered the study of biological oxidation mechanisms during the 1920s. Between 1930 and 1936, while a Professor at Szeged University, he proved that hexuronic acid, which he had previously isolated, is identical with vitamin C and that it could be…
Read More
In 1897, Dr. Alice Hamilton (1869-1970) came to Hull-House, a social settlement founded to address the needs of immigrants living on Chicago’s Near West Side. Through living and working in the Hull-House neighborhood, she identified occupational diseases plaguing those who worked in the “…
Read More
When Georgia chemist Charles Holmes Herty found a way to make quality paper from pine trees in 1932, he also founded an industry that brought much-needed jobs to the depression-crippled south. Paper producers had deemed the plentiful pine too gummy—until Herty's Savannah Pulp and Paper…
Read More
The Chemical Abstracts Service, a division of the American Chemical Society, has provided the most comprehensive repository of research in chemistry and related sciences for over 100 years. CAS innovations have fueled chemical research through development of the CAS RegistrySM and CAS databases…
Read More
Recent archaeological evidence reveals early Virginia, which included both the Roanoke and Jamestown colonies, as the birthplace of the American chemical enterprise. Chemical processes first applied experimentally at Roanoke were re-introduced at Jamestown twenty years later.
…
Read More
Imagine a world without batteries. It would be a much different world, in which the automobile and the telephone would have developed differently and probably later, a world without many of the conveniences of modern life and without some of the necessities. The battery, ever smaller and more…
Read More
By the 1950s, synthetic fabrics - often wrinkle resistant and flame retardant - began to overtake cotton as the dominant U.S. textile fiber. To reverse this trend chemists and chemical engineers at the Southern Regional Research Center initiated research to modify cotton chemically. Their…
Read More
DayGlo fluorescent pigments, a new class of pigments based on fluorescent dyes and polymeric materials, were developed between the 1930s and 1950s by scientists at Switzer Brothers, Inc. (now Day-Glo Color Corp.). These pigments absorb various light frequencies (visible and invisible to the…
Read More
Long before Texas gushers and offshore drilling, and a century before oil wells dotted Arabian sands and rose out of Venezuelan waters, the center of petroleum production was western Pennsylvania. In the middle of the 19thcentury two developments occurred that guaranteed Pennsylvania’s dominance…
Read More

