Developed by Rohm and Haas in the 1940s, water-based acrylic emulsion technology filled a need for easy-to-use household paints for a growing suburban population in the United States following World War II. This aqueous technology required less preparation to use, was easier to clean up, had less odor, and performed better than or equal to paints made with solvents. It was also a leap forward in acrylic chemistry.
ACS


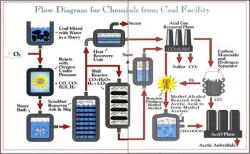
Chemicals from the Coal Facility of Eastman Chemical Company was the first in the United States to use coal rather than petroleum as a raw material in the commercial production of acetyl chemicals — important building blocks in the synthesis of a wide range of consumer products. The plant, located in Kingsport, Tennessee, began operation in 1983 after more than a decade of planning and construction, prompted by the oil embargoes of the 1970s.

The Williams-Miles History of Chemistry Collection, established in 1992, is one of the leading historical collections of chemistry books in the southern United States. It represents a combined 70 years of scholarly collecting by Wyndham D. Miles, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, and William D. Williams, Professor of Chemistry at Harding University. More than 2,000 volumes published between 1600 and 1900 are preserved here; the collection is particularly strong in 19th-century works.

This research and development complex was established by the founders of Universal Oil Products (later named UOP) to develop key products for the oil-refining industry. The processes created here profoundly affected the refining, treatment and conversion of crude oil and the development of the petroleum and petrochemical industries. Conceived as a combination of quiet academic retreat and industrial plant, Riverside attracted many of the world's leading petroleum scientists and a dedicated support team. Between 1921 and 1955, Riverside research resulted in 8,790 U.S. and foreign patents.

In the years 1926 to 1956, the German chemist Hermann Staudinger carried out his pathbreaking research on macromolecular chemistry in Freiburg. His theories on the polymer structures of fibers and plastics and his later research on biological macromolecules formed the basis for countless modern developments in the fields of materials science and biosciences and supported the rapid growth of the plastics industry. For his work in the field of polymers, Staudinger was awarded the Nobel Prize for chemistry in 1953.

In 1900, Moses Gomberg, Professor of Chemistry at the University of Michigan, confirmed the existence of a stable, trivalent organic free radical: triphenylmethyl. In so doing, he challenged the then prevailing belief that carbon could have only four chemical bonds. Gomberg’s discovery made a major contribution to theoretical organic chemistry and fostered a field of research that continues to grow and expand. Today, organic free radicals are widely used in plastics and rubber manufacture, as well as medicine, agriculture and biochemistry.

For more than a century, scientists at Rockefeller University have enhanced our understanding of the molecular basis of life — specifically the relationship between the structure and function of nucleic acids and proteins. They showed that DNA transfers genetic information and that the sugars ribose and deoxyribose are the key building blocks of the nucleic acids RNA and DNA.

In 1962 Neil Bartlett demonstrated the first reaction of a noble gas. The noble gas family of elements - helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon - had previously been regarded as inert. By combining xenon with a platinum fluoride, Bartlett created the first noble gas compound. This reaction began the field of noble gas chemistry, which became fundamental to the scientific understanding of the chemical bond. Noble gas compounds have helped create anti-tumor agents and have been used in lasers.

When Joseph Priestley discovered oxygen in 1774, he answered age-old questions of why and how things burn. An Englishman by birth, Priestley was deeply involved in politics and religion, as well as science. When his vocal support for the American and French revolutions made remaining in his homeland dangerous, Priestley left England in 1794 and continued his work in America until his death. His library of some 1,600 volumes and his chemical laboratory, where he first isolated carbon monoxide, were probably the best in the country at that time.
Innovations
The story is so improbable it defies belief: a soil sample from Japan stops suffering in Africa. It starts when a scientist discovers a lowly bacterium near a golf course outside Tokyo. A team of scientists in the United States finds that the bacterium produces compounds that impede the activity…
Read More
Flavor—encompassing both aroma and taste—provides the defining characteristic of how we experience food. Flavor has long been an enigma to scientists: Aristotle described two categories of taste, sweet and bitter. Today we recognize five basic tastes in food: sweetness, saltiness, sourness,…
Read More
Instant mashed potatoes are commonplace on grocery shelves and have found wide use institutionally and in domestic and international food aid programs. The most successful form of instant mashed potatoes resulted from the flake process developed in the 1950s and 1960s at the Eastern Regional…
Read More
Frozen foods have become a staple of the modern diet. Freezing allows consumers to have access to foods previously unavailable or available only seasonally, and it provides convenience for many families. But frozen foods became commonplace only after World War II, in part due to research…
Read More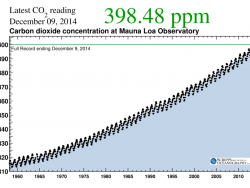
Charles David Keeling of Scripps Institution of Oceanography was the leading authority in establishing the global atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) record. In 1958, Keeling began measuring atmospheric CO2 concentrations from Hawaii’s Mauna Loa Observatory. Using rigorous analytical procedures,…
Read More
As much as we know today about the planets of the solar system, it’s almost incomprehensible that a mere 50 years ago we knew almost nothing about them. Observations of even Mars and Venus, Earth’s closest planetary neighbors, through Earth-based telescopes had provided only the most rudimentary…
Read More
Izaak Maurits Kolthoff (1894–1993) has been described as the father of modern analytical chemistry for his research and teaching that transformed the ways by which scientists separate, identify, and quantify chemical substances. Once a collection of empirical recipes and prescriptions, the field…
Read More
The American Chemical Society, the world’s largest scientific society, celebrated its 125th anniversary in 2001. Founded in 1876 in New York City, the Society now has 186 local sections in all 50 states, international chapters, and 32 technical divisions that bring together scientists with…
Read More
Rachel Carson’s Silent Spring, published in 1962, was a landmark in the development of the modern environmental movement. Carson’s scientific perspective and rigor created a work of substantial depth and credibility that sparked widespread debate within the scientific community and the…
Read MorePrior to its merger with the Carnegie Institute of Technology in 1967 to form Carnegie Mellon University, the nonprofit Mellon Institute for Industrial Research was a major, independent research corporation dedicated to promoting applied research for industry and educating scientific researchers…
Read More
The federal government’s first physical science research laboratory was chartered by Congress on March 3, 1901, as the National Bureau of Standards, which became the National Institute of Standards and Technology in 1988. Recognizing the critical importance of chemical measures and standards,…
Read More

