In 1794, the Delaware legislature authorized a lottery to fund the erection of ice piers in the harbor at New Castle. The ice harbor was designed to protect anchored ships from storms and ice. At the time, New Castle served as the principal winter port for ships from the Port of Philadelphia because ice on the Delaware River posed such a serious hazard to the wooden-hulled vessels. The harbor was the first of its type on the river and the last one to be maintained as the need for them declined. It served as a model for the other four harbors constructed in the area.
ASCE

Delaware 19709New CastleState: DECountry: USAWebsite: http://www.asce.org/Project/New-Castle-Ice-Harbor/Creator: Delafield, Richard

Navajo Bridge spans Marble Canyon, 470 feet above the Colorado River in Grand Canyon National Park. It was considered the highest steel arch bridge in America when completed.
The Navajo Bridge (also known as the Grand Canyon Bridge) was built in 1929 by the Arizona Highway Department and provided a vital transportation link over the Grand Canyon between northern Arizona and southern Utah. Construction commenced by building on one side of the canyon, then on the other, until the two sides met in the middle.
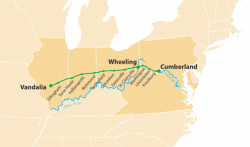
The National Road was the first interstate highway in the United States, and the first roadway to be financed with federal money. Authorized by Congress during the administration of Thomas Jefferson in 1806, the road was built over time and in sections from Cumberland, Maryland, westward through the states of Pennsylvania, Virginia (now West Virginia), Ohio, and Indiana, before terminating at the state capital of Vidalia, Illinois.

The Mullan Road was designed to facilitate the movement of troops and supplies across the Rocky Mountains between the Missouri River basin in the Great Plains and the Columbia River Basin at the Columbia Plateau during times of Indian hostilities. But because peace was reached with the Northwest Indians early on, the road was used only once (in 1860) for military means. Instead, it became a popular thoroughfare for emigrants and fortune-seekers during the Montana and Idaho gold rushes of the 1860s.

Designed, patented, and built by Thomas W.H. Moseley, this arched 96-foot span bridge preceded by years the standard use of wrought iron for bridges. For the first time in the United States, Moseley incorporated the use of riveted wrought-iron plates for the triangular-shaped top chord.

Just 20 years after settling the uninhabited Salt Lake valley, Brigham Young and his Mormon followers completed one of the nation's most impressive public structures. The 9,000-seat Mormon Tabernacle boasts a clear span roof measuring 150 feet by 250 feet, its timber trusses joined with wooden pegs and lashed with green rawhide, which shrank and tightened as it dried.

The Memphis Bridge (now called the Frisco Bridge) comprises three spans across the Mississippi River. With a main span measuring over 790 feet, it was one of the longest railroad bridges in the world upon completion. The renowned George Morison, after whom the bridge is unofficially named, served as Chief Engineer.

Known as "the highest and lowest holing in history," the tunnel bored through the Rockies at an elevation of 9,200 feet, 2,800 feet below the surface. Eight hundred men worked around the clock for 3 1/2 years, moving 3 billion pounds of rock.

Minot's Ledge is a wave-swept rock formation in a rocky area of ocean about a mile off the Cohasset shore near Boston. Numerous serious shipwrecks prompted the government to erect a beacon there, and construction began in the summer of 1847.
The light, constructed on tall iron legs, was put into operation on January 1, 1850. Designers believed that the water would flow freely through the legs, leaving the lighthouse intact. But a terrible winter storm toppled it in 1851, killing the two assistant keepers.

This was America's first large-scale activated sludge plant. The successful operation of Milwaukee's sewage treatment plant led the way for many other American municipalities to adopt its methods of efficient environmental recycling.
Prior to 1925, sewage and industrial waste from the City of Milwaukee and its suburbs (then population 500,000) was discharged to the Milwaukee, Menomonee, and Kinnickinnic rivers, which converge in Milwaukee and flow together through a single outlet into Lake Michigan.
Innovations

The voyage of Captain George Vancouver, 1791 -1795, was commissioned by the British Admiralty to map in detail the west coast of North America from Mexico to Alaska and to meet with Spanish authorities on the coast to enforce the terms of the Nootka Sound Convention of 1790.
Departing…
Read More
The Royal Colonial Boundary of 1665 was decreed by England's King Charles II to demarcate his American colonies. It provided a survey from the Atlantic Ocean to the Mississippi River along 36 degrees, 30 minutes north latitude. The boundary now serves to divide Virginia from North Carolina and…
Read More
The "Land Ordinance of 1785" required that U.S. lands in the public domain be surveyed before sale, and that the surveys be made in accordance with a consistent, integrated system of lines grid-oriented to a true meridian (north-south reference line) and base line (east-west reference line),…
Read More
Amos Eaton and Stephen Van Rensselaer founded the Rensselaer School for "the application of science to the common purposes of life" in 1824. Eaton had practiced surveying as a teenager building his own compass and chain and wrote an early book on surveying. Later he studied law before becoming…
Read More
Until 1900, the Chicago River drained into Lake Michigan, along with all the sewage from the city; and the Des Plaines River west of Chicago emptied into the Illinois River, which eventually flows to the Mississippi. Chicago residents drew their drinking water from polluted areas of the lake…
Read More
On October 23rd, 1852 a notice was sent to practitioners of civil engineering in and near New York City requesting their participation in developing an association that would serve the professionals who design and construct America's built environment. Twelve men responded to this invitation,…
Read More
Taken together, the 1940 and 1950 Tacoma Narrows bridges mark a significant turning point in the design of long-span suspension bridges. The original 1940 structure was designed with one of the shallowest and narrowest stiffening elements of any long-span suspension bridge yet built. The…
Read More
The Dalles Lock and Dam was one of the largest, most complete, and complex multipurpose projects of its kind in the United States at the time of its construction. It provided an example for future projects benefitting navigation, recreation, water for irrigation and hydropower, fish migration,…
Read MoreThe roof system of this building, designed by Lev Zetlin and opened in 1960, was the first of its kind in the world. Before the mid-1950's, the use of long-span cable structures was generally limited to suspension bridges. The only other significant cable roof structure preceding the Utica…
Read More
The Union Bridge was built in 1804 by Theodore Burr and was the first to cross the lower section of the Hudson River connecting Waterford and Lansingburg, New York. The wooden bridge's key feature was the arch that started below the deck at the abutments and ran near the top of the top chord at…
Read More
With the dawn of the automobile age at the beginning of the Twentieth Century, the entire nation started to demand better roads. In the 1910s, motorists and businessmen in Utah became aware of the possibilities of tourism as a business. Soon the state of Utah and the federal government responded…
Read More
In the 1940s and 1950s, New Orleans experienced growth. Unfortunately, access from the north to the City continued to be limited by Lake Pontchartrain. Driving around the Lake was a time consuming effort. During this time period, a renewed interest developed to provide a direct connection across…
Read More
"It remains today one of the great bridge engineering accomplishments for railway and highway bridges built in the country."
- Historic American Engineering Record, Southeast Regional Office, National Park Service, U.S. Department of the Interior, 2005
By the late 1880s, New…
Read More
Spearheaded by Chief Engineer William J. Wilgus and constructed under challenging conditions with no interruption of existing train service, Grand Central Terminal was a triumph of innovative engineering in the design of urban transportation centers. Its novel, two-level station, made possible…
Read MoreThe confluence of the Mohawk and Hudson rivers was the site of distinct advances in transportation of the early 19th Century. The Erie Canal in 1825 and the Mohawk and Hudson Railroad in 1831 were both of national significance.
The Erie Canal started at a boat basin in Albany. It…

The Titan is a 200-ton electrically driven hammerhead cantilever crane, the earliest survivor of this type. It is now all that remains of the once great John Brown Shipyard in Clydebank near Glasgow where many of the world's great ships were built. Designed and constructed by Sir William Arrol…
Read More

