ASME


Wisconsin Historical SocietyImage Caption: East Wells Onieda Street Power PlantEra_date_from: 1918



The Chicago, Burlington, & Quincy Railroad was the first railroad to link Chicago and the Mississippi River, in the 1850s. This forty-stall roundhouse, large even for its time, became a major center for railroad activity for the CB&Q. It served as a repair and construction facility from which more locomotives and cars than any other CB&Q installation were built. Steam engines, passenger cars, freight cars, precision parts, tools, and machines were designed and built, beginning about 1858.
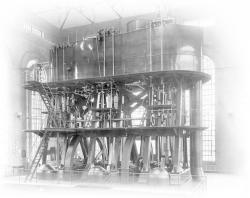
At the site of the first water pumping station providing water and sewage systems to the City of Erie in 1868, the Chestnut Street Pumping Station houses one of the largest steam engines, which pumped 20 million gallons a day. The triple-expansion steam reciprocating engine, which pumped water from the filter plant to the city reservoir, was typical of those used in municipal water pumping stations throughout the country during the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries.


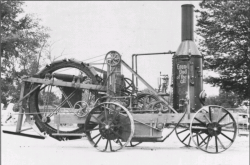
During the post-Civil War era, efforts to cultivate the land for higher crop yields resulted in the digging of thousands of miles of ditches to improve land drainage. Accurately graded ditches were needed for open drainage, pipeline trenches and placement of underground agricultural drainage tile. Teams of skilled workers laid out the direction and gradient of a ditch and dug it out with pick and shovel. The Black Swamp area, where Lake Erie drains into northwest Ohio and southeast Michigan, was the center of much of the U.S. ditching activity.




