The Ashuelot Covered Bridge is located at the center of Ashuelot, NH. It is a Town lattice truss bridge, spanning the Ashuelot River in a roughly north-south orientation. It consists of two spans with a total length of 178 feet (54 m). The total width of the bridge is 29 feet (8.8 m), and has a central roadway and sidewalks (measuring 3'10" in width) on each side. The bridge rests on stone abutments and a central pier. The abutments have been reinforced with concrete since the bridge was built, and the central pier has been protected by a metal breakwater.
USA
Ackley Bridge is an excellent example of a multiple kingpost truss and a noteworthy early example of covered bridge preservation efforts in the United States. Built in 1832 by Joshua Ackley (b.1805) and Daniel Clouse (b.1812), Ackley Bridge originally spanned Enslow’s Branch of Wheeling Creek between Greene County and Washington County in Pennsylvania, where it carried traffic for over a century.

Design Concepts For Vegetated Waterways - Historic Landmark of Agricultural Engineering Rainfall runoff causes severe gully erosion on unprotected lands and has ruined thousands of U S acres in the past. Concepts were developed at this site for vegetation-lined waterways that now safely convey runoff water from millions of acres.Engineers of the US Soil Conservation Service (SCS) initiated studies on hydraulics of vegetated waterways at an outdoor laboratory near Spartanburg, South Carolina, in 1935. Under the directions of W. O.

The Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE) was developed at the USDA National Runoff and Soil Loss Data Center at Purdue University in a national effort led by Walter H. Wischmeier and Dwight D. Smith. The USLE was published in 1965 in USDA Agriculture Handbook 282.
A = average annual soil loss (in tons/acre)
R = rainfall erosivity index
K = soil erodibility factor
LS = topographic factor
C = cropping factor
P = conservation practice factor

In 1942, University of California, Davis (UCD) biologist, Jack Hanna recognized the need for breeding tomato varieties that ripen uniformly and withstand the rigors of mechanical harvesting. In 1949, UCD agricultural engineer Coby Lorenzen and Hanna began developing a mechanical tomato harvester. Parallel efforts by others, notably those started in 1957 by agricultural engineer Bill Stout and horticulturist Stan Ries of Michigan State University, eventually resulted in several different harvesting mechanisms. In the late 1950s, UCD agricultural engineer Steven J.

First Tower Silo Designated A Historic Landmark Of Agricultural Engineering. The First Tower Silo In America Was Erected Near This Site On The Hatch Farm, One Half-Mile East Of Spring Grove, Illinois. Fred L. Hatch And His Father, Lewis Hatch, Erected This Silo In October 1873, After Fred Graduated From The Illinois Industrial University. (Now The University Of Illinois). Textbooks On Agriculture Were Scarce, And Professor Willard F. Bliss Translated French And German Pamphlets On Silage Production Wherein The Entire Corn Plant Was Buried In Pits, And This Inspired Young Hatch.

Since 1948, over 11,000 dams and associated conservation practices in more than 2,000 watershed projects encompassing 160 million acres in 47 states have been constructed as a part of the USDA Small Watershed Program. These projects have improved the quality of life and the environment in rural communities by protecting people's lives and property, conserving soil and water resources, reducing flooding, providing economic development, recreation, and water supplies, enhancing water quality, and improving wetlands and wildlife habitat.

The object of the Red Wing project was "To determine the optimum economic uses of electricity in agriculture and to study the value of electricity in improved living conditions on the farm." Although not the first service to farms in the U.S., it was likely the first built as an experiment specifically for collecting and publishing engineering and economic data.
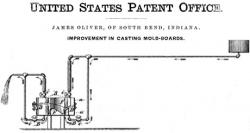
On June 30, 1857, James Oliver filed a patent application for chilling the wear face of cast-iron moldboard plows. While pouring molten cast iron in sand molds he circulated hot water through chillers to regulate the rate of cooling. Oliver's control of raw material content and cooling produced moldboards with a very hard surface and a softer, tough inner core for strength. Their fine textured wearing faces of uniform hardness maintained a mirror polish and resisted rust.

In 1894, Dr. John Harvey Kellogg and his brother, Will Keith (W.K.) Kellogg, were making a granola type cereal for their patients in the Battle Creek Sanitarium, a general health facility in Michigan. This granola cereal was made from wheat that was boiled, rolled into a sheet, toasted, and ground. They accidentally left a batch of boiled wheat stand overnight before passing it through the rolls. The individual grains were subsequently pressed into flakes which were toasted to form the first flaked cereal. Two years later, W.K. Kellogg made the first corn flakes.
Innovations

Much of the sophisticated system of canals, dams, gates, and tunnels built to manage water power in 19th-century Lowell is preserved today as the basis of the Lowell National Historical Park and the Lowell Heritage State Park. Pictured above is the Boott Penstock, an early channel adjacent to…
Read More
In the 18th century, French architect Claude-Nichols Ledoux was known for forging architectural beauty with industrial efficiency. One hundred years later his vision was given new life through the design of the Louisville Water Company Pumping Station. Inspired by Ledoux's Royal Salt Works at…
Read More
Most of the locks were 184 feet long and 36 feet wide, able to handle boats up to 160 feet long. The sandstone locks (along with wood miter gates, rock-filled timber-crib dams and bypass canals with guard gates) created a slackwater navigation system stretching over 90 miles.
…

People thought inventor Walter Aiken was crazy when he proposed a railway to the top of Mt. Washington. Aiken built a model of the roadbed and track with a cog rail system, but entrepreneur Sylvester Marsh is credited for launching the Cog Railway and bringing Aiken's ideas to fruition.
… Read More
In the mid-1800s Virginia City was America's greatest producer of high-grade silver and gold ore. When mining activities began, natural springs provided water to the camps. As the population grew, the Virginia and Gold Hill Water Company was formed to address the need for more water. The company…
Read MoreThis machine, which began operation on December 15, 1891, for the New York Edison Illuminating Company, represents the beginning of large-scale electric power generation in the United States. The generator was designed by chief engineer John Van Vleck, David Joy (known in England for his valve…
Read More
This run-of-the-river plant is a typical example of late nineteenth-century small-scale (750 kilowatt) low-head hydroelectric power technology. The Fries Manufacturing and Power Company began operating the Idol's Station on April 18, 1898, making it the first commercial hydroelectric plant in…
Read More
This low-head operating plant is representative of nineteenth-century hydropower-plant practice using many small turbines in contrast to twentieth-century use of few large turbines and generators. Its 40,000 horsepower capacity made it the largest in the country using turbines of American design…
Read More
Only since 1912 have glass jars and bottles been in cheap and plentiful supply for pharmaceuticals, household products, food and beverages, and an endless variety of uses. The bottle-making machine introduced the safety, standardization, quality, and convenience of glass containers. Not only did…
Read More
Spearheaded by Hugh Cooper, the Keokuk Dam & Power Plant served as a prototype for many future power plants. The project harnessed the hydropower of the Mississippi River, between Keokuk, Iowa and Hamilton, Illinois.
The crest of the dam is nearly a mile long. The dam structure…
Read More
The 1.6-mile Holland Tunnel was the first underwater vehicular crossing of the Hudson River and the first tunnel specifically designed for automobiles and trucks. It dramatically reduced the time required to traverse the Hudson River, a trip previously possible only by ferry.
A major…
Read More
The largest mine hoist in the world, it serves the two incline skipways of Shaft No. 2, almost 9,300 feet long. The overhead winding drum has a diameter of 30 feet, of which the cylindrical center section is 10 feet long. The two 10-foot long end sections taper down to a 15-foot diameter. Wire…
Read More
The Connecticut Light & Power Company pioneered the use of pumped storage in the United States at this hydroelectric station. First operated in 1929, the Rocky River Plant had two reversible pumps that somewhat resemble large hydroelectric turbines. This permitted significant improvements in…
Read More
The Miami Conservancy District flood control project was the direct result of the disastrous flood of 1913, when waters from the Miami, Stillwater, and Mad rivers flooded Dayton and surrounding communities in the Miami Valley. More than 400 lives were lost and property damage exceeded $100…
Read More
America's first practical helicopter, it pioneered the single main rotor concept that became the predominant helicopter configuration throughout the world. The principles that were developed and demonstrated by the VS-300 had direct application in the design of the early mass-production…
Read MoreThe Wildcat's innovative "Sto-Wing" mechanism developed on the XF4F-4 prototype by Leroy (Roy) Grumman (1895-1982), a founder of Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation, was crucial to the U. S. Navy's success during World War II.
The idea of a folding wing was not new: as early as 1920…
Read More
Maine's heavy snows led turnpike maintenance personnel to bring "left-handed" snow plows into prominence. By using left-handed and traditional right-handed plows in tandem, they were able to distribute snow more evenly - an important advance that has been emulated by many highway maintenance…
Read More
Developed for use in both the plains and mountains, this coal-fired passenger locomotive was among the most advanced in design, construction, and performance of any 4-8-4. Designed by Norfolk & Western engineers and built in the Norfolk & Western Roanoke shops, the 611 was specially…
Read More
The 4,620-horsepower GG1 was primarily a passenger locomotive, routinely operating at over 100 miles per hour, but was used in freight service as well. Conceived by the Pennsylvania Railroad and built by the Baldwin Locomotive Works and General Electric Company, No. 4800 logged nearly 5 million…
Read More
The articulated wheel-base steam locomotive represents the final phase of steam locomotive development in size and power. The cab-in-front feature was widely used by the Southern Pacific Railroad beginning in 1909 to alleviate smoke and heat problems for locomotive personnel en route through…
Read More

