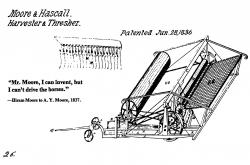
A Historic Landmark of Agricultural Engineering in 1834 Near the Village of Climax, Michigan, Hiram Moore and John Hascall Built and Put Into Practical Use the First Successful Grain Combined Harvester - Thresher Which was Patented June 28, 1836. This Achievement was a Significant Contribution to the Development of American Agriculture Dedicated by the American Society of Agricultural Engineers 1978
USA

Designated A Historic Landmark Of Agricultural Engineering The Massey-Harris No. 20 was the First Commercially- Successful Self-Propelled Combine Used to Harvest Small Grains Under a Wide Variety of Conditions, World-Wide. Engineered By Thomas Carroll, Chief Engineer, Aided by Robert Ashton and Albert Luke, Principal Assistants, it was First Marketed in 1938 by the Massey-Harris Company. This Combine Opened a New Era an Farm Mechanization and Revolutionized the Grain Harvesting Process. Forty-Four Years Later, This Same Harvesting Principle Continues to be Used Throughout the World.

Luebben Hay Baler - Historic Landmark of Agricultural Engineering. In 1892, Hugh Luebben from Sutton, Nebraska, with sons Melchior and Ummo built a mobile machine to produce round hay bales between two sets of rotating flat belts. They began manufacturing the baler in 1909 in Beatrice and later moved to Omaha, Nebraska. Allis-Chalmers purchased the patent in 1939 and eventually sold 77,200 "Roto-Balers." The Luebben baler made handling easier, improved hay quality, and reduced costs. The same basic design is used on modern large round balers.

The first laser grade control was developed by agricultural engineers James Fouss and Norman Fausey of USDA's Agricultural Research Service at The Ohio State University in the mid-1960's. That system controlled the precise depth and grade of subsurface drains by regulating trenching and plow-type drainage machines. Photo cells mounted on the drainage machine automatically raised and lowered the digging device, keeping the cells centered on a laser beam set to the desired elevation and grade.
matic grade‐control system on the plow.

On this site in 1837 John Deere built the first successful self-scouring steel plow, thereby making a significant contribution to the development of American agriculture. Dedicated by American Society of Agricultural Engineers 1976
In 1926, Ives Hall, the original Agricultural Engineering Building at The Ohio State University, Columbus, was designated as ASAE's first engineering landmark in honor of department founder and 18th president of ASAE Fredrick Walter Ives. Frederick W. Ives 1884 - 1924.
Ives Hall was on the corner of Neil and Woodruff Avenues from 1926 - 2002. This display has been constructed with brick from the original structure.

In 1892, John H. Froehlich, Froehlich, IA, Mounted A Gasoline Fueled Internal Combustion Engine On A Traction Geared Frame And Used It To Power A Threshing Machine. A Change In Power Source Had Begun On North American Farms. In 1892, The Case Co., Racine, Wi, Built An Experimental Gas Traction Engine. In 1898 A Patent Was Issued To The Van Duzen Co. Cincinnati, OH, For A Gasoline Traction Engine. Huber Mnfg., Marion, Oh, Bought This Patent In 1898 And Produced 30 Prototype Units. In 1902, Hart-Parr, Founded By Charles W. Hart And Charles H.


Near This Location In The 1930's James E. Love And Horace D. Hume Of Garfield, Washington, Invented The Flexible Floating Cutterbar And The Tined Pickup Reel To Harvest Low-Growing, Fragile Crops. These Devices Were Developed For The Local Crops Of Dry Peas And Lentils And Were Then Adopted Nationwide To Soybeans And Other Low-Growing Crops That Tangle And Lodge. These Mechanisms Reduced Dry Pea Harvesting Costs By 28% And Crop Loss From 50 To 10%. These Inventions Were Reported To Save The Equivalent Of 2,750,000 Acres Of Soybeans Annually.

The Sidehill Combine Developed By The Holt Brothers At Stockton, California In 1891, A Significant Milestone In Grain Harvesting And Agricultural Efficiency That Opened New Land For Wheat Farming, Is Designated A Historic Landmark Of Agricultural Engineering By The American Society Of Agricultural Engineers 1982
Innovations

Built by the Bay City Dredge Works of Bay City, Michigan, this dredge was used to construct a portion of US 41 called the Tamiami Trail, which connected Tampa with Miami through the Everglades and Big Cypress Swamp. The last remaining display of walking dredges (of some 145 walking machines), it…
Read More
The longest steel-arch bridge in the world for 46 years, the Bayonne Bridge continues to be celebrated today as a major aesthetic and technical achievement. The 1,675-foot bridge replaced a ferry service which until then was the only means of crossing from the Bayonne peninsula to Staten Island…
Read More
Montogomery Bell was a land developer and iron maker who purchased the Harpeth Narrows site to expand his industrial empire - which ultimately consisted of 14 iron blast furnaces throughout middle Tennessee.
The Harpeth River makes a tight bend around a steep limestone ridge, losing 17…
Read More

Belle Fourche, meaning "Beautiful Forks" in French, refers to the confluence of the Redwater and Belle Fourche Rivers. The gold rush to the Black Hills in 1876 brought many people to the area, but agriculture and livestock soon became the principal industries. Farmers and civic leaders…
Read More
The St. Petersburg Yacht Basin was the original operating location of the St. Petersburg – Tampa Airboat Line, the nation’s first, regularly-scheduled commercial airline. The line’s inaugural flight was on January 1, 1914, with two daily, round-trip flights between St. Petersburg, Fla., and…
Read More
The first known pumping system providing drinking and wash water in the North American colonies. The building (still standing) is dated 1761, but it was preceded by an experimental frame building dated 1754. Before the Bethlehem built its system, assigned carriers would daily haul water up the…
Read More
Soon after gold was discovered at Sutter's Mill near Sacramento in 1848, General John Bidwell found gold near the Middle Fork of the Feather River. His discovery brought hordes of miners to the scene and Bidwell Bar was born. The Bidwell Bar Suspension Bridge over the Feather River was one of…
Read More

All building materials were made fire-resistant to protect against incendiary bombing. Treatment involved a vacuum process of salt impregnation. During construction, high winds caused a partial collapse of some members. The ruined materials were piled for incineration, but would not burn; so the…
Read More
Nicholas Montgomery Powers built the bridge. It was first constructed behind the village, then taken apart and reassembled over the stream. Some residents questioned the idea of re-constructing it, but Powers was so confident of the bridge's durability that he sat on the roof when the final…
Read More

By the 1890s, the transportation infrastructure of downtown Boston - a maze of narrow, winding streets laid out, in some cases, along Colonial cow paths - proved completely inadequate for the needs of a modern, bustling metropolis. Tremont Street, the city's main thoroughfare, was regularly…
Read More


A product of the Northern California Gold Rush, the Bridgeport Covered Bridge is believed to be the longest, single-span, wooden covered bridge in the United States. Crossing the south fork of the Yuba River at a span of 233 feet, the bridge was built by the Virginia City Turnpike Company as…
Read More
On May 24, 1883, with schools and businesses closed for the occasion, New York celebrated the opening of the Brooklyn Bridge. Also known as the Great East River Bridge, it was built over 14 years in the face of enormous difficulties. Deaths, fire in the Brooklyn caisson, and a scandal over…
Read More
In its infancy, Hangar Nine housed Curtiss JN-4s ("Jennys") like the one Charles Lindbergh landed there when he reported for duty as a flying cadet in 1924.
As the U.S. was preparing to enter World War I, the Army raced to build an entire airfield, complete with 16 wooden hangars,…
Read More



