Brothers Cyril and Louis Keller designed and built the first small, lightweight, three-wheel, front-end loader in their machinist-blacksmith shop in Rothsay, Minnesota. A local farmer wanted to mechanize cleaning manure from his obstacle-filled, two-story turkey barn. The machine, first used in 1957, was able to turn completely around within its own length. Melroe Manufacturing Company, Gwinner, ND purchased the rights to the Keller loader and hired the Kellers to continue development of the loader in 1958.
1957


Frozen foods have become a staple of the modern diet. Freezing allows consumers to have access to foods previously unavailable or available only seasonally, and it provides convenience for many families. But frozen foods became commonplace only after World War II, in part due to research conducted at the Western Regional Research Center which helped determine the proper time and temperature at which various foods should be frozen to insure their quality and stability.
The plaque commemorating the research reads:


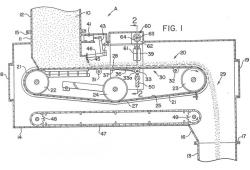
A variety of mechanical feeders, including drag-chain conveyors and rotary pocket feeders, historically have been used to volumetrically control the flow of fuel to coal pulverizers on power generators. Most power generation in the United States has relied on burning fossil fuels in steam boilers, with coal as the fuel of choice. By the 1920s, pulverized-firing (the burning in suspension of finely ground coal particles) evolved as means to more complete fuel combustion and higher system efficiencies and facilitated the use of larger boilers.



Founded in 1957, Raychem Corporation was the first company to successfully apply the new science of radiation chemistry to commercial use. This accomplishment led to the creation of tough new materials and high-performance products such as irradiated polyethylene insulated wire and heat-shrinkable tubing through the crosslinking of polymeric materials.
Innovations

Founded in 1957, Raychem Corporation was the first company to successfully apply the new science of radiation chemistry to commercial use. This accomplishment led to the creation of tough new materials and high-performance products such as irradiated polyethylene insulated wire and heat-…
Read More

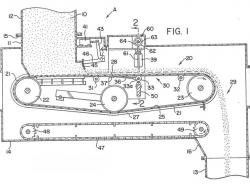
A variety of mechanical feeders, including drag-chain conveyors and rotary pocket feeders, historically have been used to volumetrically control the flow of fuel to coal pulverizers on power generators. Most power generation in the United States has relied on burning fossil fuels in steam…
Read More


Frozen foods have become a staple of the modern diet. Freezing allows consumers to have access to foods previously unavailable or available only seasonally, and it provides convenience for many families. But frozen foods became commonplace only after World War II, in part due to research…
Read More
Brothers Cyril and Louis Keller designed and built the first small, lightweight, three-wheel, front-end loader in their machinist-blacksmith shop in Rothsay, Minnesota. A local farmer wanted to mechanize cleaning manure from his obstacle-filled, two-story turkey barn. The machine, first…
Read More

