"Eads had to succeed in the face of conventional wisdom which doomed him to disaster. Entrenched authorities not only completely dismissed his theories, but pointed to the indifferent European experiences with what he proposed."
- ASCE Landmark Nomination Proposal, 1982
Civil

The Dublin to Belfast Rail Link established a vital connection between the capitals of Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland. The line's most notable engineering feature was the 1,760-foot-long Boyne Bridge; it represented one of the earliest uses of calculated stresses, the first large-scale use of wrought iron latticed girders, and the first full scale test of continuous beams. Tests performed on the wrought iron columns and struts were published and provided invaluable information for engineers who would design similar structures in the future.
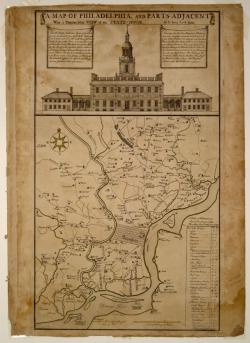
The City Plan of Philadelphia is a seminal creation in American city planning in that it was the first American City Plan to provide open public squares for the free enjoyment of the community and a gridiron street pattern featuring streets of varying widths: wide main streets and narrower side streets. In addition this plan was the first city plan in the United States to provide for long-term urban growth. These features inspired the planners of many cities to adopt the Philadelphia Plan as a model.

Constructed to provide a safe, potable water supply for the citizens of Chicago, Ellis Chesbrough's Chicago Water Supply System was the first major system to utilize offshore intake systems. The system includes the landmark Chicago Water Tower and the Chicago Avenue Pumping Station. Its subaqueous tunnel was a pioneering effort in American civil engineering.

Designed by William A. Truesdell, a railroad engineer, the Seventh Street Improvement Arches celebrates the engineering application of mathematics to improve living conditions.

Between 1825 and 1847 the State of Ohio constructed 1,000 miles of canals and feeder canals, 33,000 acres of reservoir surface area, 29 dams across streams, 294 lift locks, 44 aqueducts and many smaller structures at a cost of about 16 million dollars. The network of navigable canals provided a system of economical transportation where none had previously existed; the young state, with its isolated frontier lifestyle, was transformed almost overnight into a thriving segment of the nation's economy.
Chartered in 1825, the Louisville and Portland Canal Company was authorized to construct a canal around the rapids called the "Falls of the Ohio." Construction started on March 1, 1826. The canal and first generation of locks were completed in 1830. As originally constructed, the canal was 1.9 miles long, 64 feet wide, and terminated at its lower end with a three-flight lock system with a total lift of 26 feet. Each lock chamber was 198 feet long between miter posts, with available length for vessels of 183 feet, width of 52 feet, and a lift at low stages of 8.5 feet.

Historically, a camino real (Royal Road) is defined as a road that connects Spanish capital with Spanish capital, a distinction not shared with roads connecting ordinary Spanish or Indian villages. The term Camino Real implied that the status and privileges granted to the villas and capitals it connected were extended to the main routes of travel through use by officials and others acting in the interest of the crown. Unlike ordinary Indian and Spanish villages, villas like San Antonio and others along the route had charters that prescribed royal privileges.

The first Zuiderzee Enclosure Dam ran from North Holland to the island of Wieringen, successfully barring the sea for over 50 years and protecting a large area north of Amsterdam. The total Zuiderzee project was the largest land reclamation effort in the Netherlands, developed over a period of about 80 years, beginning in 1918 and reaching completion in 1996. The huge dyke/dam was considered one of the greatest engineering feats of its time.

With the discoveries of South Africa's diamonds in the 1860s and gold in the 1880s, immigrants flooded into Cape Town and changed it into a major commercial center. Unfortunately, its water supply had not kept pace with the population growth. After several droughts and years of inadequate water supply, the Woodhead Tunnel was constructed between 1887 and 1891. When it failed to solve the water shortage problem, the Municipality of Cape Town determined that a dam and reservoir needed to be built.
Innovations

Developed by the Hohokam, a prehistoric group of Native Americans, the canal system in the Salt River Valley serviced more than 100,000 acres of mostly arid desert country in what is now southern Arizona. The prehistoric Hohokam constructed one of the largest and most sophisticated irrigation…
Read More
In 1918, the U.S. Reclamation Service's director and chief engineer Arthur P. Davis proposed a dam of unprecedented height to control the devastating floods on the Colorado River, generate hydroelectric power, and store the river's ample waters for irrigation and other uses. A dam project of…
Read More
The 50-mile Houston Ship Channel is a manmade port for ocean-going vessels, stretching from the Gulf of Mexico to Houston and Harris County, Texas.
The waterway was originally known as Buffalo Bayou and was swampy, marshy, and overgrown with dense vegetation. Steamboats and…

Built between 1794 and 1796 by the 22nd King of the Joseon Dynasty, Jeongio, this fortress is an outstanding example of early modern defensive works. Principally designed by Jeong Yak-Yong, it incorporated the most highly developed features of science and engineering from both the east and west…
Read More
When completed in 1888 to a height of 90 feet, Sweetwater Dam was once the tallest masonry arch dam in the United States, and it led to many others of the same basic design. The original construction began in November 1886 under the direction of Frank E. Brown (civil engineer for Bear Valley Dam…
Read More
The 16-story Ingalls Building, still in use today, was the world's first reinforced concrete skyscraper. Its success led to the acceptance of high-rise concrete construction in the United States.
Melville E. Ingalls, for whom the building is named, spent two years convincing city…
Read More
In 1866, the Covington and Cincinnati Suspension Bridge was the largest suspension bridge in the world. Also called the Ohio Bridge, it was officially renamed the John A. Roebling Bridge in 1983. It was the first permanent bridge over the Ohio River and the only public project in America…
Read More
The Kamehameha V Post Office is the oldest surviving public building in the U.S. constructed with reinforced concrete. The success of this early structure helped establish the value of reinforced concrete as a durable construction material.
Brickmaker J.G. Osborne was chosen to provide…
Read More
Built during the 1930s, when Argentina's economy was the tenth strongest in the world, the Kavanagh Building was one of the world's first reinforced concrete skyscrapers and for many years remained the tallest building in South America. Commissioned by Corina Kavanagh and designed by architect…
Read More
A 214-foot single-span covered wooden bridge, built above the cribs of stone in the AuSable River that served to break log jams and ice floes, collapsed during the winter of 1875 under the weight of a three-foot snowfall and high winds. The "Upper Bridge" (pictured) was built in its place.…
Read More
The Charles River Basin was one of the pioneering environmental engineering projects in America. The project transformed 675 acres of unhealthy and unsightly salt marshes and tidal flats were into an environmental centerpiece for the Boston area by 1910. This was one of the first public projects…
Read More
When Governor James Grant arrived in the newly acquired British colony of East Florida in 1764, he found it devoid of settlers. To increase both the population and commerce with the 13 colonies to the north, he commanded that a road be built from his provincial capital of St. Augustine to Ft.…
Read More
The workforce consisted of less than 100 men, yet they finished construction in just 94 days. Such speed was possible due to the elimination of scaffolding. Instead, iron rods were used to support construction of the trusses between the towers, and workers moved back and forth across the rods. A…
Read MoreThe Lake Moeris Quarry Road, in the Faiyum District of Eygpt, is the oldest road in the world of which a considerable part of its original pavement is still preserved. This road was used to help transport the heavy blocks of basalt from the quarry 43 miles southwest of Cairo to the royal…
Read More
Some of the station's notable achievements:
The first method for detecting radioactive particles in water supplies
A successful system of slow-sand filter beds for drinking water
The landmark demonstration that microorganisms carried within filter media could degrade…

In the 1850s, the Lexington and Danville Railroad began building a suspension bridge over the Kentucky River. The bridge was designed by John A Roebling. Due to unforeseen increases in train loads, the Roebling bridge was never completed. The High Bridge would then be built 20 years later on the…
Read More
Ancient Chinese literature refers to the Zhaozhou Bridge as a "crescent moon rising from the clouds" or a "rainbow in the sky." Throughout its history, it has been known as the Anchi or Anji Bridge (literally "safe crossing"), the Dashi Bridge ("big stone"), and the Dashiqiao ("great stone")…
Read More
Machu Picchu represents the culmination of Inca public works building standards and technology, as well as 4,000 years of Andean community development. This landmark is the most well known archaeological site in South America and serves as a destination site for world travelers. It was a royal…
Read More
The Mackinac (pronounced "Mack-in-awe") Bridge (1957) spans the Straits of Mackinac between Lake Michigan and Lake Huron, connecting the Lower and Upper peninsulas of Michigan. Prior to the construction of the bridge, a fleet of nine ferries would carry as many as 9,000 vehicles per day, with…
Read More
When opened in 1909, the 1,470 foot long main span of the Manhattan Bridge was the third longest suspension bridge span in the world, after the nearby Brooklyn and Williamsburg Bridges. The Manhattan Bridge has two 725 foot long suspended side spans for an overall length of 2,920 feet. The…
Read More

