This research and development complex was established by the founders of Universal Oil Products (later named UOP) to develop key products for the oil-refining industry. The processes created here profoundly affected the refining, treatment and conversion of crude oil and the development of the petroleum and petrochemical industries. Conceived as a combination of quiet academic retreat and industrial plant, Riverside attracted many of the world's leading petroleum scientists and a dedicated support team. Between 1921 and 1955, Riverside research resulted in 8,790 U.S. and foreign patents.
1920-1929


Beech Factory Landing FieldWichitaState: KSZip: 67206Country: USAWebsite: https://www.aiaa.org/HistoricAerospaceSites/Creator: Cessna, Clyde , Beech, Walter
The Travel Air Airplane Manufacturing Company served as the incubator in which Wichita Kansas’ present-day status as the world’s “Air Capital” first developed. The firm was among the first viable airplane manufacturers to be established in Wichita (1925). It also was responsible for four aviation legends firmly establishing themselves in Wichita and forming the nexus between Wichita and world aviation: Walter Beech, Olive Ann Mellor (later Olive Ann Beech), Clyde Cessna, and Lloyd Stearman.


In the years 1926 to 1956, the German chemist Hermann Staudinger carried out his pathbreaking research on macromolecular chemistry in Freiburg. His theories on the polymer structures of fibers and plastics and his later research on biological macromolecules formed the basis for countless modern developments in the fields of materials science and biosciences and supported the rapid growth of the plastics industry. For his work in the field of polymers, Staudinger was awarded the Nobel Prize for chemistry in 1953.

In May 1927, the same month of Charles A. Lindbergh's famous transatlantic flight from New York to Paris, a fact-finding commission appointed by the U.S. Secretary of Commerce concluded that Newark would be the ideal location for an airfield to serve the greater New York/New Jersey metropolitan area.
Civic leaders wasted no time; construction began on the Newark Airport in January 1928. Nine months and $1,750,000 later, 68 acres of soggy marshland had been filled and converted to an airport.

Navajo Bridge spans Marble Canyon, 470 feet above the Colorado River in Grand Canyon National Park. It was considered the highest steel arch bridge in America when completed.
The Navajo Bridge (also known as the Grand Canyon Bridge) was built in 1929 by the Arizona Highway Department and provided a vital transportation link over the Grand Canyon between northern Arizona and southern Utah. Construction commenced by building on one side of the canyon, then on the other, until the two sides met in the middle.

Known as "the highest and lowest holing in history," the tunnel bored through the Rockies at an elevation of 9,200 feet, 2,800 feet below the surface. Eight hundred men worked around the clock for 3 1/2 years, moving 3 billion pounds of rock.



Wind dynamics were a major consideration in building such a huge structure. When winds blow against the building, they are deflected up over the roof, creating a partial vacuum that can draw the roof up with a force several times greater than the direct force of the wind. Wind tunnel testing on a model helped designers decide that a semi-parabolic shape would best resolve air current concerns.
Innovations

Designated an Historic Landmark of Agricultural Engineering. In the Shelbyville Area During the Spring of 1929, Raymore McDonald Designed and Developed the First Commercial Pick-Up Baler as Conceived and Financed by Horace Tallman and His Sons, Leslie R. and Gentry L. These Balers were…
Read More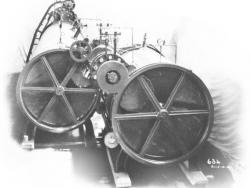
The Food Canning Industry Was Revolutionized In 1920, When The Continuous Rotary Pressure Sterilizer Was Introduced By Albert R. Thompson. Thompson Was Chief Engineer For The Anderson-Barngrover Co. Of San Jose, California, Now The FMC Corporation. The Sterilizer Cooked Canned Products…
Read MoreIn 1926, Ives Hall, the original Agricultural Engineering Building at The Ohio State University, Columbus, was designated as ASAE's first engineering landmark in honor of department founder and 18th president of ASAE Fredrick Walter Ives. Frederick W. Ives 1884 - 1924.
Ives Hall was on…
Read More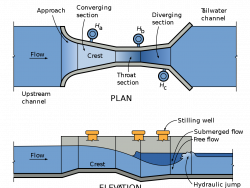
Since the beginning of irrigated agriculture, it has been important to measure flows of irrigation water. Accuracy of early water measurement methods often suffered because of trash or sediment in the water, or unusual flow conditions. Ralph L. Parshall saw this problem when he began…
Read More
Early tractors were massive and expensive. Their steel lug wheels gave poor traction and a rough ride. Lugs were prohibited on many roads. 1926 Hoyle Pounds modified a Fordson tractor with zero pressure truck tires on special rims to improve performance on sandy soils in Winter…
Read More
The Edger station was the first steam electric plant produced that could tolerate over 1000 psi of pressure. Initially conceived by Mr. Irving Edwin Moultrop, then Assistant Superintendent, Construction Bureau of the Edison Electric Illuminating Company of Boston. He guided his company and the…
Read More

