The Miami Conservancy District flood control project was the direct result of the disastrous flood of 1913, when waters from the Miami, Stillwater, and Mad rivers flooded Dayton and surrounding communities in the Miami Valley. More than 400 lives were lost and property damage exceeded $100 million. When Dayton flooded, great fires raged, adding to the devastation. Many believed that the area would never recover.
1920-1929

- Concrete Conduit
- Dry Dam
- Earth-Core
- Flood Control
- Flood Prevention Committee
- Great Depression
- Levee
- Mad River
- Miami Conservancy District
- Miami River
- Retardation Basin
- Stillwater River
- 1920-1929
- 1922
- 1972
- 45424
- ASCE
- Civil
- Flood Prevention Committee
- Great Dayton Flood
- Morgan, Arthur Ernest
- OH
- USA
- Water Supply & Control

The Connecticut Light & Power Company pioneered the use of pumped storage in the United States at this hydroelectric station. First operated in 1929, the Rocky River Plant had two reversible pumps that somewhat resemble large hydroelectric turbines. This permitted significant improvements in the system efficiency of the company's network of hydroelectric and thermal-electric power generating plants. Water is pumped uphill through a penstock and stored in Lake Candlewood.

The largest mine hoist in the world, it serves the two incline skipways of Shaft No. 2, almost 9,300 feet long. The overhead winding drum has a diameter of 30 feet, of which the cylindrical center section is 10 feet long. The two 10-foot long end sections taper down to a 15-foot diameter. Wire hoisting ropes (almost 27 tons) could be wound onto a small end of the cylindrical drum as the other rope unwound from the cylindrical section.

The 1.6-mile Holland Tunnel was the first underwater vehicular crossing of the Hudson River and the first tunnel specifically designed for automobiles and trucks. It dramatically reduced the time required to traverse the Hudson River, a trip previously possible only by ferry.
A major difficulty when tunneling beneath a river is to keep water and mud from inundating the workers and equipment in the tunnel. Builders of the Holland Tunnel used a shield that enveloped the work site as the excavation progressed; this also avoided obstruction of shipping traffic during construction.

The introduction of penicillin in the 1940s, which began the era of antibiotics, has been recognized as one of the greatest advances in therapeutic medicine. The discovery of penicillin and the initial recognition of its therapeutic potential occurred in the United Kingdom, but, due to World War II, the United States played the major role in developing large-scale production of the drug, thus making a life-saving substance in limited supply into a widely available medicine.
The plaque commemorating the event reads:

In brilliant collaboration, Carl and Gerty Cori studied how the body metabolizes glucose and advanced the understanding of how the body produces and stores energy. Their findings were particularly useful in the development of treatments for diabetes. In 1947 the Coris shared a Nobel Prize for their discoveries.
The plaque commemorating the event reads:

In 1899, during the earliest days of the automobile revolution, A. O. Smith developed a new, lightweight steel car frame. Within a few short years, he was selling these frames to a “who’s who” of car makers including Cadillac, Oldsmobile, and Ford. A. O. Smith’s son, Lloyd Raymond, carried on the family company, expanding the automotive business and introducing the world’s first automated frame production line, the Mechanical Marvel.
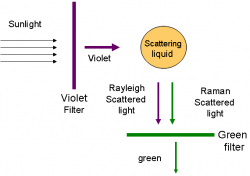
"I propose this evening to speak to you on a new kind of radiation or light emission from atoms and molecules." With these prophetic words, Professor C. V. Raman of Calcutta University began his lecture to the South Indian Science Association in Bangalore on March 16, 1928. Raman proceeded to describe a discovery that resulted from a deceptively simple experiment. Conducted far from the great centers of scientific research in the Western world, the results would capture the attention of scientists around the world and bring many accolades, including the Nobel Prize, to their discoverer.


