The Watervliet arsenal complex originally was built to house and manufacture weapons for the War of 1812. During the Civil War, it specialized in gun cartridges and artillery carriages. The facility today is a primary site for making state-of-the-art tank cannon, howitzers, mortars, and recoilless rifles.
NY


A transportation tunnel under the Hudson River connecting Manhattan and New Jersey was first considered in the 1860s, fueled by New York City's rapidly growing congestion and the inadequacy of existing ferry service to population centers across the river. DeWitt Clinton Haskin, an engineer formerly with the Union Pacific Railroad, started the project in 1874 and subsequently endured an extended lawsuit, several failures of the tunnel wall, and an exhaustion of funds before quitting in 1887 with only 1,600 feet completed.

In the 19th century, New York City was a burgeoning industrial and commercial metropolis - the largest city in the United States and second largest in the world. As the city's population increased, people began to call for construction of an underground railway. Many unusual engineering challenges had to be overcome, not the least of which was construction in a dense urban area. After lengthy legal battles over property rights and the debt limit of the city, ground was broken on March 24, 1900.

BinghamtonState: NYZip: 13905Country: USAWebsite: https://www.asme.org/about-asme/who-we-are/engineering-history/landmarks/210-link-c-3-flight-trainerCreator: Link, Edwin
During the 1920s, Edwin A. Link was employed in his father's organ building and repair business. He obtained his pilot's license in 1927 and became convinced that a mechanical device could be built as an inexpensive method to teach basic piloting. Link received three patents on his flight trainer (No. 1,825,462, March 12, 1930; No. 2,244,464, June 3, 1941; and No. 2,358,016, Sept. 12, 1944).

Tracing its history to the earliest days of powered flight – to the Wright brothers and Glenn Curtiss – the site began as the research laboratory of the Curtiss-Wright Aircraft Company. After World War II, it was donated to Cornell University, and in January 1946 opened its doors as the Cornell Aeronautical Laboratory. Nearly every military aircraft and space vehicle developed in the United States from the end of World War II until the present day has been tested at the facility, now known as Calspan.

When opened in 1903, the 1,600 foot long main span of the Williamsburg Bridge was the world's longest suspension span, surpassing the nearby Brooklyn Bridge by only 4.5 feet. The Williamsburg Bridge remained the world's longest suspension bridge span for 21 years until the opening of the Bear Mountain Bridge in 1924. The Williamsburg Bridge has two unsuspended side spans of 596.5 feet, each supported from below by trussed towers, giving the bridge an overall length of 2,793 feet. The four main suspension cables are 18.75 inches in diameter and each composed of over 10,000 wires.

The Whipple Bowstring Truss Bridge was built from a design patented in 1841 by Squire Whipple. Whipple was the first person to understand the stresses in truss members and he developed the first theoretical formula to calculate stresses in the articulated truss. His bowstring truss was the first to use cast iron for compression and wrought iron for tension membranes.

The history of this foundry, which was the oldest malleable iron company in continuous operation in the United States for many years, was inseparable from that of the small town of Westmoreland, where neighbors and workers kept time by the foundry bell. The firm was founded as Oakhill Malleable Iron Company in 1833 and was established under its present name in Westmoreland in 1850. Erastus W. Clark, who along with his brother-in-law Abel Buell brought the foundry to Westmoreland, ran the ironworks until 1871 and was the first of six generations who still own and manage it.

BrookRyeState: NYCountry: USAWebsite: http://www.asce.org/Project/Ward-House/Creator: Ward, William , Mook, Robert
It is a large, imposing structure (over a dozen rooms and spacious halls) dominated by a four-story octagonal tower at one corner and a second shorter square tower at another corner containing tanks for potable and fire-fighting water supply.

The Triborough Bridge Project is a three-branched waterway crossing that connects Manhattan, the Bronx, and Queens at a junction of the East River and the Harlem River in New York City. The complex structure includes a suspension bridge from Wards Island to Queens, a vertical lift span from Randall's Island to Manhattan, a fixed span (designed to be convertible to a lift span) across the Bronx Kills, viaducts, and an innovative three-legged roadway interchange.
Innovations

In 1794, Congress authorized and President Thomas Jefferson signed into law the raising of a Corps of Artillerists and Engineers (now the United States Army Corps of Engineers) to be educated and stationed at the newly created United States Military Academy. The U.S. Military Academy was the…
Read More

For more than a century, scientists at Rockefeller University have enhanced our understanding of the molecular basis of life — specifically the relationship between the structure and function of nucleic acids and proteins. They showed that DNA transfers genetic information and that the sugars…
Read More
A bridge across the Hudson at or near Poughkeepsie was planned starting in the early 1870s to primarily carry coal from the coalfields of northeastern Pennsylvania to New England. At the time there were no bridges between Albany and New York Harbor. Horatio Allen, soon to be President of the…
Read More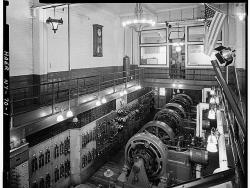
Steam and the inexpensive electricity it could produce brought about dramatic technical growth in the United States. Developed during the last century, reliable and efficient steam engines were the forerunners of today's massive generating facilities. A rare survivor of the period, the Pratt…
Read More
When opened in 1909, the Queensboro Bridge had the two longest steel cantilever spans in the world - 1,182 feet from Manhattan to Blackwell's Island and 984 feet from Blackwell's Island to Queens. These would remain the world's longest cantilever spans until the completion of the Quebec Bridge…
Read More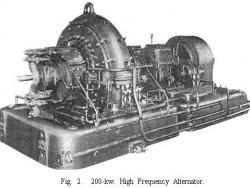

Sculptor Frederic-Auguste Bartholdi is credited with bringing the concept of the Statue of Liberty to fruition, deriving inspiration from the 19th-century penchance for grandiose monuments. He originally designed the statue for placement at the Suez Canal, but the project was never commissioned…
Read More
The Triborough Bridge Project is a three-branched waterway crossing that connects Manhattan, the Bronx, and Queens at a junction of the East River and the Harlem River in New York City. The complex structure includes a suspension bridge from Wards Island to Queens, a vertical lift span from…
Read More
It is a large, imposing structure (over a dozen rooms and spacious halls) dominated by a four-story octagonal tower at one corner and a second shorter square tower at another corner containing tanks for potable and fire-fighting water supply.
The Ward House, named for its builder William…
Read More
The history of this foundry, which was the oldest malleable iron company in continuous operation in the United States for many years, was inseparable from that of the small town of Westmoreland, where neighbors and workers kept time by the foundry bell. The firm was founded as Oakhill Malleable…
Read More
The Whipple Bowstring Truss Bridge was built from a design patented in 1841 by Squire Whipple. Whipple was the first person to understand the stresses in truss members and he developed the first theoretical formula to calculate stresses in the articulated truss. His bowstring truss was the first…
Read More
When opened in 1903, the 1,600 foot long main span of the Williamsburg Bridge was the world's longest suspension span, surpassing the nearby Brooklyn Bridge by only 4.5 feet. The Williamsburg Bridge remained the world's longest suspension bridge span for 21 years until the opening of the Bear…
Read More
Tracing its history to the earliest days of powered flight – to the Wright brothers and Glenn Curtiss – the site began as the research laboratory of the Curtiss-Wright Aircraft Company. After World War II, it was donated to Cornell University, and in January 1946 opened its doors as the Cornell…
Read More
During the 1920s, Edwin A. Link was employed in his father's organ building and repair business. He obtained his pilot's license in 1927 and became convinced that a mechanical device could be built as an inexpensive method to teach basic piloting. Link received three patents on his flight…
Read More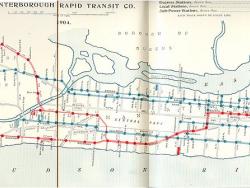
In the 19th century, New York City was a burgeoning industrial and commercial metropolis - the largest city in the United States and second largest in the world. As the city's population increased, people began to call for construction of an underground railway. Many unusual engineering…
Read More
A transportation tunnel under the Hudson River connecting Manhattan and New Jersey was first considered in the 1860s, fueled by New York City's rapidly growing congestion and the inadequacy of existing ferry service to population centers across the river. DeWitt Clinton Haskin, an engineer…
Read More
The Watervliet arsenal complex originally was built to house and manufacture weapons for the War of 1812. During the Civil War, it specialized in gun cartridges and artillery carriages. The facility today is a primary site for making state-of-the-art tank cannon, howitzers, mortars, and…
Read More

Amos Eaton and Stephen Van Rensselaer founded the Rensselaer School for "the application of science to the common purposes of life" in 1824. Eaton had practiced surveying as a teenager building his own compass and chain and wrote an early book on surveying. Later he studied law before becoming…
Read More

